前言
现在市面上有很多成熟的ORM框架,每一种框架都有其优势和不足。在众多的优秀框架中,MyBatis无论是从地位还是市场占有率都占有很大的比重。我们也有很多小伙伴想着通过阅读源码的方式来深入了解其底层原理,进而提升自己的架构能力和抽象能力。也可以将其改造优化和改造。
在我看来,想要深入了解一个框架,就要从其设计思想入手。先摸清楚它的设计思路,再根据思路去看实现细节,这样才能达到事半功倍的效果。
本博文会记录博主自己编写的一个简易的MyBatis的实现过程,希望可以对有这方面需求的小伙伴提供帮助。也是对自己学习之路的一个小小的总结。
设计思路
我们要知道,市面上的ORM框架,说白了就是对于JDBC的封装。我们用JDBC开发过软件的小伙伴,肯定会知道使用JDBC编程的一些弊端。比如操作繁琐,SQL写在代码中存在硬编码问题,冗余重复的代码很多等等。
所以,我们在开发之初,要想清楚开发的目的,也就是解决JDBC的哪些问题,以及自己的实现思路,并根据自己的实现思路先画出自己的设计图。在我们的实际编码中,切忌不要有硬编码问题。而且要面向接口编程,时刻谨记单一职责和开闭原则的设计思想。
我们先来看一段JDBC的示例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
// 加载数据库驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 通过驱动管理类获取数据库链接
connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?characterEncoding=utf-8", "root", "root");
// 定义sql语句?表示占位符
String sql = "select * from user where username = ?";
// 获取预处理statement
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
// 设置参数,第一个参数为sql语句中参数的序号(从1开始),第二个参数为设置的参数值
preparedStatement.setString(1, "tom");
// 向数据库发出sql执行查询,查询出结果集
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
// 遍历查询结果集
while (resultSet.next()) {
int id = resultSet.getInt("id");
String username = resultSet.getString("username");
// 封装User
user.setId(id);
user.setUsername(username);
}
System.out.println(user);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 释放资源
if (resultSet != null) {
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (preparedStatement != null) {
try {
preparedStatement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (connection != null) {
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}由以上代码我们可以总结以下几个问题:
- 数据库连接创建、释放频繁造成系统资源浪费,从而影响系统性能
SQL语句在代码中硬编码,造成代码不易维护,实际应用中SQL变化的可能较大,SQL变动需要改变java代码- 使用
preparedStatement向占有位符号传参数存在硬编码,因为SQL语句的WHERE条件不一定,可能多也可能少,修改SQL还要修改代码,系统不易维护 - 对结果集解析存在硬编码(查询列名),
SQL变化导致解析代码变化,系统不易维护,如果能将数据库记录封装成pojo对象解析比较方便
我们的对应解决方案如下:
- 使用连接池技术避免重复创建销毁连接
- 将
SQL语句封装在配置文件中,程序通过读取配置文件来执行操作,解决SQL硬编码问题 - 将参数也配置在配置文件中,程序通过反射技术动态匹配参数,解决参数硬编码问题
- 将解析结果配置到配置文件中,通过反射动态拼装需要的结果类型,解决查询结果转换硬编码问题
基于以上解决方案,我们的架构设计图如下图所示:
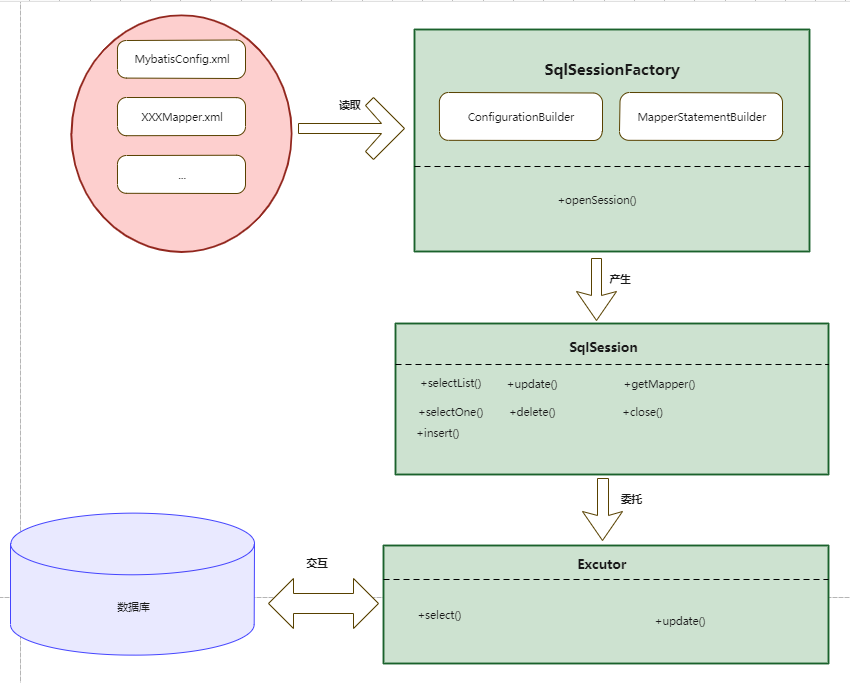
基本架构分为以上几个大的模块:
- 使用构建者模式通过读取配置文件来构建
SqlSessionFactory,并封装配置对象Configration - 通过
SqlSessionFactory对象产生SqlSession,SqlSession负责具体的增删改查的业务处理 SqlSession将与数据库的交互委托给Excutor(封装jdbc)执行
项目准备
新建一个maven工程,导入以下坐标:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.17</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>c3p0</groupId>
<artifactId>c3p0</artifactId>
<version>0.9.1.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.12</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.10</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>dom4j</groupId>
<artifactId>dom4j</artifactId>
<version>1.6.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>jaxen</groupId>
<artifactId>jaxen</artifactId>
<version>1.1.6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.16.18</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>核心配置文件格式如下:
<configuration>
<dataSource>
<property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql:///mybatis-demo"></property>
<property name="user" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="123456"></property>
</dataSource>
<mapperScan>
<property name="base-package" value="mappers"></property>
</mapperScan>
</configuration>初始化数据库sql如下:
create schema `mybatis-demo` collate utf8_general_ci;
use `mybatis-demo`;
create table dept_info
(
id int auto_increment comment '主键'
primary key,
dept_name varchar(255) default '' not null comment '部门名称',
parent_id int default 0 not null comment '上级部门id'
)
comment '部门表';
create table user_info
(
id int auto_increment comment '主键'
primary key,
username varchar(255) default '' not null comment '用户姓名'
)
comment '用户表';sql配置的mapper.xml如下:
<mapper namespace="com.rubin.mybatis.dao.IUserDao">
<select id="selectAll" resultType="com.rubin.mybatis.pojo.UserInfo">
SELECT id AS id, username AS username FROM user_info
</select>
<select id="selectByCondition" resultType="com.rubin.mybatis.pojo.UserInfo" parameterType="com.rubin.mybatis.pojo.UserInfo">
SELECT id AS id, username AS username FROM user_info WHERE username = #{username}
</select>
<insert id="insert" parameterType="com.rubin.mybatis.pojo.UserInfo">
INSERT INTO user_info(username) VALUES (#{username})
</insert>
<update id="update" parameterType="com.rubin.mybatis.pojo.UserInfo">
UPDATE user_info SET username = #{username} WHERE id = #{id}
</update>
<delete id="delete" parameterType="com.rubin.mybatis.pojo.UserInfo">
DELETE FROM user_info WHERE id = #{id}
</delete>
</mapper><mapper namespace="com.rubin.mybatis.dao.IDeptDao">
<select id="selectAll" resultType="com.rubin.mybatis.pojo.DeptInfo">
SELECT id AS id, parent_id AS parentId, dept_name AS deptName FROM dept_info
</select>
<select id="selectByCondition" resultType="com.rubin.mybatis.pojo.DeptInfo" parameterType="com.rubin.mybatis.pojo.DeptInfo">
SELECT id AS id, parent_id AS parentId, dept_name AS deptName FROM dept_info WHERE id = #{id} AND parent_id = #{parentId} AND dept_name = #{deptName}
</select>
</mapper>表映射的实体如下:
/**
* 用户信息实体
* Created by rubin on 2021/3/6.
*/
@Data
public class UserInfo implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -5092977108118253805L;
/**
* 主键
*/
private Integer id;
/**
* 用户名称
*/
private String username;
}package com.rubin.mybatis.pojo;
import lombok.Data;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* 部门信息实体
* Created by rubin on 2021/3/6.
*/
@Data
public class DeptInfo implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 6498698269763093602L;
/**
* 主键
*/
private Integer id;
/**
* 上级部门id
*/
private Integer parentId;
/**
* 部门名称
*/
private String deptName;
}Mapper接口如下:
package com.rubin.mybatis.dao;
import com.rubin.mybatis.pojo.UserInfo;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 用户接口
*/
public interface IUserDao {
/**
* 查询所有
*
* @return
*/
List<UserInfo> selectAll();
/**
* 条件查询
*
* @param userInfo
* @return
*/
UserInfo selectByCondition(UserInfo userInfo);
/**
* 插入记录
*
* @param userInfo
* @return
*/
int insert(UserInfo userInfo);
/**
* 更新记录
*
* @param userInfo
* @return
*/
int update(UserInfo userInfo);
/**
* 删除记录
*
* @param userInfo
* @return
*/
int delete(UserInfo userInfo);
}package com.rubin.mybatis.dao;
import com.rubin.mybatis.pojo.DeptInfo;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 部门接口
*/
public interface IDeptDao {
/**
* 查询所有
*
* @return
*/
List<DeptInfo> selectAll();
/**
* 根据条件查询
*
* @param deptInfo
* @return
*/
DeptInfo selectByCondition(DeptInfo deptInfo);
}代码实现
首先,我们要有一个文件读取类Resource,用来加载我们的配置文件:
/**
* 资源加载工具类
* Created by rubin on 2021/3/6.
*/
public class Resource {
/**
* 加载classpath下面的文件
*
* @param resourceLocation
* @return
*/
public static File getResource(String resourceLocation) {
String filePath = Resource.class.getClassLoader().getResource(resourceLocation).getFile();
return new File(filePath);
}
/**
* 加载classpath文件夹下面的文件列表
*
* @param folderLocation
* @return
*/
public static List<File> getResources(String folderLocation) {
File folder = getResource(folderLocation);
if (folder.isDirectory()) {
return Arrays.asList(folder.listFiles((dir, name) -> name.endsWith(".xml")));
}
throw new RuntimeException("the mapperLocation must be a folder location.");
}
}SqlSessionFactory开发
我们由SqlSessionFactory作为切入点,来依次开发相应代码,顶级接口(我们在开发过程中一定要有面向接口的思维)逻辑如下:
/**
* SqlSession工厂接口
* Created by rubin on 2021/3/6.
*/
public interface SqlSessionFactory {
/**
* 生产SqlSession
* @return
*/
SqlSession openSession() throws SQLException;
}开发我们的SqlSession顶级接口:
/**
* SqlSession接口
* Created by rubin on 2021/3/6.
*/
public interface SqlSession {
/**
* 查询列表
*
* @param mapperStatement
* @param arg
* @return
*/
<E> List<E> selectList(MapperStatement mapperStatement, Object arg) throws Exception;
/**
* 查询单条记录
*
* @param mapperStatement
* @param arg
* @return
*/
<T> T selectOne(MapperStatement mapperStatement, Object arg) throws Exception;
/**
* 插入单条记录
*
* @param mapperStatement
* @param arg
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
int insert(MapperStatement mapperStatement, Object arg) throws Exception;
/**
* 更新单条记录
*
* @param mapperStatement
* @param arg
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
int update(MapperStatement mapperStatement, Object arg) throws Exception;
/**
* 删除单条记录
*
* @param mapperStatement
* @param arg
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
int delete(MapperStatement mapperStatement, Object arg) throws Exception;
/**
* 获取mapper接口的代理类 让用户无感知的调用本地接口
*
* @param mapperClass
* @param <T>
* @return
*/
<T> T getMapper(Class<T> mapperClass);
/**
* 关闭连接
*
* @throws SQLException
*/
void close() throws SQLException;
}接下来是我们的执行器接口:
/**
* 执行器接口 目前只有查询 可扩展其他操作
* Created by rubin on 2021/3/7.
*/
public interface Executor {
/**
* 执行查询操作
*
* @param mapperStatement
* @param arg
* @return
* @throws SQLException
* @throws NoSuchFieldException
* @throws IllegalAccessException
* @throws InstantiationException
*/
<E> List<E> query(MapperStatement mapperStatement, Object arg) throws SQLException, NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException;
/**
* 执行更新数据库的操作(包括新增、修改和删除)
*
* @param mapperStatement
* @param arg
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
int update(MapperStatement mapperStatement, Object arg) throws Exception;
/**
* 关闭连接
*
* @throws SQLException
*/
void close() throws SQLException;
}封装我们的配置类,配置类里面包括我们配置的数据源信息和扫描到的所有的mapper.xml的信息封装:
/**
* 配置类
* Created by rubin on 2021/3/6.
*/
@Data
public class Configuration implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 2671465016158105857L;
/**
* 数据源
*/
private DataSource dataSource;
/**
* mapper配置集合
*/
private Map<String, MapperStatement> mapperStatementMap;
}MapperStatement实体结构如下:
/**
* mapper解析结果配置类
* Created by rubin on 2021/3/6.
*/
@Data
public class MapperStatement implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -5965608715506818980L;
/**
* 标签id 组成方式为 namespace.id
*/
private String id;
/**
* 用户自定义sql
*/
private String sql;
/**
* statementType
*/
private StatementType statementType;
/**
* 参数类型
*/
private Class<?> parameterType;
/**
* 返回类型
*/
private Class<?> resultType;
}写到这里,我们的准备工作就完成了。下面就开始我们真正意义上面的框架功能开发。我们首先先要思考,我们的SqlSessionFactory肯定是要封装我们的配置信息的。但是我们的配置信息是比较复杂的,不可能一次IO读取就可以获取到所有的信息,所以我们使用构造者模式来一步一步的构建我们的配置信息和SqlSessionFactory。
首先我们先定义Configuration的建造者ConfigurationBuilder:
/**
* 配置读取器
* Created by rubin on 2021/3/6.
*/
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
public class ConfigurationBuilder extends AbstractBuilder {
private Configuration configuration;
/**
* 根据配置文件名称读取数据源配置和映射mapper配置
*
* @param configLocation 配置文件名称 配置文件需放在classpath下面
* @throws DocumentException
* @throws PropertyVetoException
*/
public void parse(String configLocation) throws DocumentException, PropertyVetoException, ClassNotFoundException {
File configFile = getConfigFile(configLocation);
Document document = new SAXReader().read(configFile);
Element root = document.getRootElement();
readDatasource(root);
readMapperStatements(configLocation);
}
/**
* 读取mapper信息
*
* @param configLocation
*/
private void readMapperStatements(String configLocation) throws ClassNotFoundException, DocumentException {
new MapperStatementBuilder(configuration).parse(configLocation);
}
/**
* 读取数据源信息
*
* @param root
* @throws PropertyVetoException
*/
private void readDatasource(Element root) throws PropertyVetoException {
Element dataSourceElement = root.element("dataSource");
Properties properties = readElementAsProperties(dataSourceElement);
ComboPooledDataSource comboPooledDataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource();
comboPooledDataSource.setDriverClass(properties.getProperty("driverClass"));
comboPooledDataSource.setJdbcUrl(properties.getProperty("jdbcUrl"));
comboPooledDataSource.setUser(properties.getProperty("user"));
comboPooledDataSource.setPassword(properties.getProperty("password"));
configuration.setDataSource(comboPooledDataSource);
}
/**
* 获取配置文件实体
*
* @param configLocation
* @return
*/
private File getConfigFile(String configLocation) {
return Resource.getResource(configLocation);
}
}由以上代码我们可以看到,我们的配置读取分为两步,分别为读取数据源配置信息和读取所有的mapper文件的配置信息。按照单一职责的设计思想,我们定义MapperStatement的构建器MapperStatementBuilder:
/**
* 解析mapper的构造器
* Created by rubin on 2021/3/6.
*/
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
public class MapperStatementBuilder extends AbstractBuilder {
private Configuration configuration;
/**
* 解析配置文件 加载mapper到配置实体中
*
* @param configLocation
* @throws DocumentException
* @throws ClassNotFoundException
*/
public void parse(String configLocation) throws DocumentException, ClassNotFoundException {
Element root = new SAXReader().read(Resource.getResource(configLocation)).getRootElement();
Element mapperScanElement = root.element("mapperScan");
Properties properties = readElementAsProperties(mapperScanElement);
parseList(properties.getProperty("base-package").replace(".", "/"));
}
/**
* 解析mapper文件列表
*
* @param mapperBasePackage
* @throws ClassNotFoundException
* @throws DocumentException
*/
public void parseList(String mapperBasePackage) throws ClassNotFoundException, DocumentException {
List<File> mapperFiles = Resource.getResources(mapperBasePackage.replace(".", "/"));
if (mapperFiles == null || mapperFiles.size() == 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("the mapper xml file is not exist.");
}
parseList(mapperFiles);
}
/**
* 根据mapper文件实体列表解析成配置实体列表
*
* @param mapperFiles
* @throws DocumentException
* @throws ClassNotFoundException
*/
private void parseList(List<File> mapperFiles) throws DocumentException, ClassNotFoundException {
for (File mapperFile : mapperFiles) {
parseFile(mapperFile);
}
}
/**
* 解析mapper文件实体为配置实体
*
* @param mapperFile
* @throws DocumentException
* @throws ClassNotFoundException
*/
private void parseFile(File mapperFile) throws DocumentException, ClassNotFoundException {
Document document = new SAXReader().read(mapperFile);
Element root = document.getRootElement();
String namespace = root.attributeValue("namespace");
for (StatementType statementType : StatementType.values()) {
List<Element> statementElements = root.selectNodes("//" + statementType.getNode());
if (statementElements == null || statementElements.size() == 0) {
continue;
}
for (Element statementElement : statementElements) {
parseStatementElement(statementElement, namespace, statementType);
}
}
}
/**
* 解析select标签
*
* @param selectElement
* @param namespace
* @throws ClassNotFoundException
*/
private void parseStatementElement(Element selectElement, String namespace, StatementType statementType) throws ClassNotFoundException {
String id = selectElement.attributeValue("id"),
sqlText = selectElement.getTextTrim();
Class<?> parameterType = getClass(selectElement.attributeValue("parameterType")),
resultType = getClass(selectElement.attributeValue("resultType"));
MapperStatement mapperStatement = new MapperStatement();
mapperStatement.setId(id);
mapperStatement.setSql(sqlText);
mapperStatement.setStatementType(statementType);
mapperStatement.setParameterType(parameterType);
mapperStatement.setResultType(resultType);
if (configuration.getMapperStatementMap() == null) {
configuration.setMapperStatementMap(new HashMap<>());
}
configuration.getMapperStatementMap().put(namespace + "." + id, mapperStatement);
}
/**
* 获取配置的类类型
*
* @param className
* @return
* @throws ClassNotFoundException
*/
private Class<?> getClass(String className) throws ClassNotFoundException {
if (className == null) {
return null;
}
return Class.forName(className);
}
}上述代码没有什么难点,主要是熟悉一下xml文件的读取就可以。
由两个读取类我们抽离出公用部分:
/**
* 抽象建造器 抽离公用逻辑
* Created by rubin on 2021/3/25.
*/
public abstract class AbstractBuilder {
/**
* 读取节点下面所有的property属性并封装成Properties返回
*
* @param element
* @return
*/
public Properties readElementAsProperties(Element element) {
List<Element> propertyElementList = element.elements("property");
Properties properties = new Properties();
propertyElementList.stream().forEach(propertyElementItem -> {
String name = propertyElementItem.attributeValue("name"),
value = propertyElementItem.attributeValue("value");
properties.setProperty(name, value);
});
return properties;
}
}完成了该步骤之后,我们的Configuration对象就构建完成,下一步就开始我们的SqlSessionFactory的构建者的开发。我们先定义一个默认的SqlSessionFactpry的实现类:
/**
* SqlSession工厂的默认是实现类
* Created by rubin on 2021/3/6.
*/
@Data
public class DefaultSqlSessionFactory implements SqlSessionFactory {
private Configuration configuration;
private ConnectionFactory connectionFactory;
private String mapperBasePackage;
public DefaultSqlSessionFactory() {
}
public DefaultSqlSessionFactory(Configuration configuration, ConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
this.configuration = configuration;
this.connectionFactory = connectionFactory;
}
public void setMapperBasePackage(String mapperBasePackage) {
this.mapperBasePackage = mapperBasePackage;
}
/**
* 生产SqlSession
*
* @return
*/
@Override
public SqlSession openSession() throws SQLException {
SqlSession sqlSession = new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, connectionFactory);
return sqlSession;
}
/**
* 初始化方法 便于容器调用
*
* @throws ClassNotFoundException
* @throws DocumentException
*/
public void init() throws ClassNotFoundException, DocumentException {
new MapperStatementBuilder(configuration).parseList(mapperBasePackage);
}
}创建我们的构建者:
/**
* SqlSession工厂构造器
* Created by rubin on 2021/3/6.
*/
@Data
public class SqlSessionFactoryBuilder {
private Configuration configuration;
public SqlSessionFactoryBuilder() {
this.configuration = new Configuration();
}
/**
* 构造SqlSession工厂
* 包括:
* 1、 读取配置信息
* 2、 创建SqlSessionFactory默认实体
*
* @param configLocation
* @return
* @throws DocumentException
* @throws PropertyVetoException
* @throws ClassNotFoundException
*/
public SqlSessionFactory build(String configLocation) throws DocumentException, PropertyVetoException, ClassNotFoundException {
ConfigurationBuilder configurationBuilder = new ConfigurationBuilder(configuration);
configurationBuilder.parse(configLocation);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(configuration, new ConnectionFactoryBuilder().build(configuration.getDataSource()));
return sqlSessionFactory;
}
}由上述代码我们可以观察到,我们却少了一个ConnectionFactory的创建。在此,我先说一下这个ConnectionFactory的作用。这个ConnectionFactory主要是生产Connection来提供给Excutor来执行JDBC的操作,可能有的小伙伴看到这里会有疑问:为什么不直接用dataSource来生产连接,而是单独拿出来呢?其实我们是为了之后的声明式事务管理做准备。
声明式事务相信我们大家都不陌生,在生活工作中多多少少都会用到。那么他的实现原理是什么呢?我们猜测一下。最粗粒度的实现原理,就是让我们的同一线线程中的所有对于数据库的操作都基于一个连接来进行。那么,我们就可以通过这个连接来控制一个线程中所有数据库操作的事务一致了。
那么,我们怎么保证同一个线程中的所有对于数据库的操作都是用同一个数据库连接呢?我们都知道,使用ThreadLocal就能很好的实现我们的需求。在请求来的时候,我们在工厂里面获取一个连接放在ThreadLocal中,之后的所有数据库操作均从此ThreadLocal中获取连接,则实现了连接的在同一线程的一致性。
好了,补充知识讲完之后,我们着手开发ConnectionFactory:
/**
* 连接的产生工厂
* Created by rubin on 2021/3/24.
*/
public interface ConnectionFactory {
/**
* 生产Collection
*
* @return
*/
Connection getConnection();
}开发其默认实现类:
/**
* 默认的连接工厂
* Created by rubin on 2021/3/24.
*/
public class DefaultConnectionFactory implements ConnectionFactory {
public DataSource dataSource;
public DefaultConnectionFactory() {
super();
}
public DefaultConnectionFactory(DataSource dataSource) {
this.dataSource = dataSource;
}
/**
* 生产Collection
*
* @return
*/
@Override
public Connection getConnection() {
try {
return dataSource.getConnection();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}开发构建者:
/**
* 连接工厂建造器
* Created by rubin on 2021/3/25.
*/
public class ConnectionFactoryBuilder {
/**
* 构建连接工厂
*
* @param dataSource
* @return
*/
public ConnectionFactory build(DataSource dataSource) {
return new DefaultConnectionFactory(dataSource);
}
}至此,我们关于SqlSessionFactory的开发以及顶级接口的准备就完成了。
SqlSession开发
我们先实现一个SqlSession的默认实现类:
/**
* SqlSession默认实现类
* Created by rubin on 2021/3/6.
*/
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
public class DefaultSqlSession implements SqlSession {
private Configuration configuration;
private Executor executor;
public DefaultSqlSession(Configuration configuration, ConnectionFactory connectionFactory) throws SQLException {
this.configuration = configuration;
this.executor = new DefaultExecutor(connectionFactory);
}
/**
* 查询列表
*
* @param mapperStatement
* @param arg
* @return
* @throws SQLException
* @throws InstantiationException
* @throws IllegalAccessException
* @throws NoSuchFieldException
*/
@Override
public <E> List<E> selectList(MapperStatement mapperStatement, Object arg) throws Exception {
List<E> results = executor.query(mapperStatement, arg);
return results;
}
/**
* 查询单条
*
* @param mapperStatement
* @param arg
* @return
* @throws SQLException
* @throws NoSuchFieldException
* @throws InstantiationException
* @throws IllegalAccessException
*/
@Override
public <T> T selectOne(MapperStatement mapperStatement, Object arg) throws Exception {
List<Object> objects = selectList(mapperStatement, arg);
if (objects == null) {
return null;
}
if (objects.size() == 1) {
return (T) objects.get(0);
}
throw new RuntimeException("there are too many result.");
}
/**
* 插入单条记录
*
* @param mapperStatement
* @param arg
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public int insert(MapperStatement mapperStatement, Object arg) throws Exception {
return executor.update(mapperStatement, arg);
}
/**
* 更新单条记录
*
* @param mapperStatement
* @param arg
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public int update(MapperStatement mapperStatement, Object arg) throws Exception {
return executor.update(mapperStatement, arg);
}
/**
* 删除单挑记录
*
* @param mapperStatement
* @param arg
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public int delete(MapperStatement mapperStatement, Object arg) throws Exception {
return executor.update(mapperStatement, arg);
}
/**
* 获取mapper接口的代理类
*
* @param mapperClass
* @param <T>
* @return
*/
@Override
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> mapperClass) {
T t = (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(DefaultSqlSession.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{mapperClass}, (proxy, method, args) -> {
String methodName = method.getName(),
className = method.getDeclaringClass().getName(),
id = className + "." + methodName;
MapperStatement mapperStatement = configuration.getMapperStatementMap().get(id);
Object arg = null;
if (args != null && args.length > 0) {
arg = args[0];
}
switch (mapperStatement.getStatementType()) {
case SELECT:
return handleSelect(method, mapperStatement, arg);
case INSERT:
return handleInsert(mapperStatement, arg);
case UPDATE:
return handleUpdate(mapperStatement, arg);
case DELETE:
return handleDelete(mapperStatement, arg);
default:
return null;
}
});
return t;
}
/**
* 处理查询操作
*
* @param method
* @param mapperStatement
* @param arg
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
private Object handleSelect(Method method, MapperStatement mapperStatement, Object arg) throws Exception {
Type returnType = method.getGenericReturnType();
if (returnType instanceof ParameterizedType) {
return selectList(mapperStatement, arg);
}
return selectOne(mapperStatement, arg);
}
/**
* 处理插入操作
*
* @param mapperStatement
* @param arg
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
private Object handleInsert(MapperStatement mapperStatement, Object arg) throws Exception {
return insert(mapperStatement, arg);
}
/**
* 处理更新操作
*
* @param mapperStatement
* @param arg
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
private Object handleUpdate(MapperStatement mapperStatement, Object arg) throws Exception {
return update(mapperStatement, arg);
}
/**
* 处理删除操作
*
* @param mapperStatement
* @param arg
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
private Object handleDelete(MapperStatement mapperStatement, Object arg) throws Exception {
return delete(mapperStatement, arg);
}
/**
* 关闭连接
*
* @throws SQLException
*/
@Override
public void close() throws SQLException {
executor.close();
}
}/**
* SqlStatement的类型枚举类
* Created by rubin on 2021/3/15.
*/
@Getter
@AllArgsConstructor
public enum StatementType {
/**
* 查询
*/
SELECT("select"),
/**
* 修改
*/
UPDATE("update"),
/**
* 添加
*/
INSERT("insert"),
/**
* 删除
*/
DELETE("delete");
String node;
}我们的SqlSession是委托了Excutor来做的操作。这里只是封装了调用逻辑以及代理接口的获取逻辑。
Excutor开发
首先还是老套路,开发默认的Excutor实现类:
/**
* 默认的执行器
* Created by rubin on 2021/3/7.
*/
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
public class DefaultExecutor implements Executor {
private ConnectionFactory connectionFactory;
/**
* 执行查询操作
*
* @param mapperStatement
* @param arg
* @return
* @throws SQLException
* @throws NoSuchFieldException
* @throws IllegalAccessException
* @throws InstantiationException
*/
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MapperStatement mapperStatement, Object arg) throws SQLException, NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException {
BoundSql boundSql = parseCustomSql(mapperStatement.getSql());
final PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connectionFactory.getConnection().prepareStatement(boundSql.getSql());
setParam(boundSql, mapperStatement, preparedStatement, arg);
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
List<Object> resultList = parseQueryResult(resultSet, mapperStatement);
if (resultList == null) {
return new ArrayList<>();
}
return (List<E>) resultList;
}
/**
* 更新单条记录
*
* @param mapperStatement
* @param arg
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public int update(MapperStatement mapperStatement, Object arg) throws Exception {
BoundSql boundSql = parseCustomSql(mapperStatement.getSql());
final PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connectionFactory.getConnection().prepareStatement(boundSql.getSql());
setParam(boundSql, mapperStatement, preparedStatement, arg);
return preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
}
/**
* 关闭连接
*
* @throws SQLException
*/
@Override
public void close() throws SQLException {
connectionFactory.getConnection().close();
}
/**
* 设置参数
*
* @param boundSql
* @param mapperStatement
* @param preparedStatement
* @param arg
* @throws NoSuchFieldException
* @throws IllegalAccessException
* @throws SQLException
*/
private void setParam(BoundSql boundSql, MapperStatement mapperStatement, PreparedStatement preparedStatement, Object arg) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException, SQLException {
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
if (parameterMappings != null && parameterMappings.size() > 0) {
if (arg == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("arg can not be null.");
}
for (int i = 0, iLength = parameterMappings.size(); i < iLength; i++) {
String paramName = parameterMappings.get(i).getContent();
Field field = mapperStatement.getParameterType().getDeclaredField(paramName);
field.setAccessible(true);
Object fieldValue = field.get(arg);
preparedStatement.setObject(i + 1, fieldValue);
}
}
}
/**
* 解析查询结果
*
* @param resultSet
* @param mapperStatement
* @return
* @throws SQLException
* @throws IllegalAccessException
* @throws InstantiationException
* @throws NoSuchFieldException
*/
private List<Object> parseQueryResult(ResultSet resultSet, MapperStatement mapperStatement) throws SQLException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException, NoSuchFieldException {
List<Object> results = new ArrayList<>();
while (resultSet.next()) {
ResultSetMetaData metaData = resultSet.getMetaData();
Class resultType = mapperStatement.getResultType();
Object resultItem = resultType.newInstance();
// 此处特别注意!从1开始遍历
for (int i = 1, iLength = metaData.getColumnCount(); i <= iLength; i++) {
// 此处使用metaData.getColumnLabel(i)解决别名问题
String columnName = metaData.getColumnLabel(i);
Field field = resultType.getDeclaredField(columnName);
field.setAccessible(true);
Object fieldValue = resultSet.getObject(i);
field.set(resultItem, fieldValue);
}
results.add(resultItem);
}
return results;
}
/**
* 解析用户的自定义sql为jdbc标准sql 并顺序封装占位参数名称
*
* @param sql
* @return
*/
private BoundSql parseCustomSql(String sql) {
ParameterMappingTokenHandler parameterMappingTokenHandler = new ParameterMappingTokenHandler();
GenericTokenParser genericTokenParser = new GenericTokenParser("#{", "}", parameterMappingTokenHandler);
String parseSql = genericTokenParser.parse(sql);
BoundSql boundSql = new BoundSql(parseSql, parameterMappingTokenHandler.getParameterMappings());
return boundSql;
}
}这里我们的执行逻辑就是JDBC的一套逻辑,查询步骤如下:
- 编译我们的自定义
SQL,将我们的变量用?替换并记录其位置,并封装传入参数 - 执行
SQL查询,得到查询结果 - 根据Mapper中配置的结果类型,封装成要求的实体并返回
修改(包括新增、编辑和删除)的步骤如下:
- 编译我们的自定义
SQL,将我们的变量用?替换并记录其位置,并封装传入参数 - 执行修改
SQL,返回影响行数
由此,我们定义如下实体类,用来封装我们转换后的SQL以及参数:
/**
* 解析用户的自定义sql后的实体封装
* Created by rubin on 2021/3/7.
*/
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
public class BoundSql {
/**
* jbdc标准sql
*/
private String sql;
/**
* 用户自定义sql占位参数集合
*/
private List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings;
}@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
public class ParameterMapping {
private String content;
}转换工具类如下:
/**
* @author Clinton Begin
*/
public interface TokenHandler {
String handleToken(String content);
}/**
* @author Clinton Begin
*/
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
public class GenericTokenParser {
private final String openToken; //开始标记
private final String closeToken; //结束标记
private final TokenHandler handler; //标记处理器
/**
* 解析${}和#{}
* @param text
* @return
* 该方法主要实现了配置文件、脚本等片段中占位符的解析、处理工作,并返回最终需要的数据。
* 其中,解析工作由该方法完成,处理工作是由处理器handler的handleToken()方法来实现
*/
public String parse(String text) {
// 验证参数问题,如果是null,就返回空字符串。
if (text == null || text.isEmpty()) {
return "";
}
// 下面继续验证是否包含开始标签,如果不包含,默认不是占位符,直接原样返回即可,否则继续执行。
int start = text.indexOf(openToken, 0);
if (start == -1) {
return text;
}
// 把text转成字符数组src,并且定义默认偏移量offset=0、存储最终需要返回字符串的变量builder,
// text变量中占位符对应的变量名expression。判断start是否大于-1(即text中是否存在openToken),如果存在就执行下面代码
char[] src = text.toCharArray();
int offset = 0;
final StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
StringBuilder expression = null;
while (start > -1) {
// 判断如果开始标记前如果有转义字符,就不作为openToken进行处理,否则继续处理
if (start > 0 && src[start - 1] == '\\') {
builder.append(src, offset, start - offset - 1).append(openToken);
offset = start + openToken.length();
} else {
//重置expression变量,避免空指针或者老数据干扰。
if (expression == null) {
expression = new StringBuilder();
} else {
expression.setLength(0);
}
builder.append(src, offset, start - offset);
offset = start + openToken.length();
int end = text.indexOf(closeToken, offset);
while (end > -1) {////存在结束标记时
if (end > offset && src[end - 1] == '\\') {//如果结束标记前面有转义字符时
// this close token is escaped. remove the backslash and continue.
expression.append(src, offset, end - offset - 1).append(closeToken);
offset = end + closeToken.length();
end = text.indexOf(closeToken, offset);
} else {//不存在转义字符,即需要作为参数进行处理
expression.append(src, offset, end - offset);
offset = end + closeToken.length();
break;
}
}
if (end == -1) {
// close token was not found.
builder.append(src, start, src.length - start);
offset = src.length;
} else {
//首先根据参数的key(即expression)进行参数处理,返回?作为占位符
builder.append(handler.handleToken(expression.toString()));
offset = end + closeToken.length();
}
}
start = text.indexOf(openToken, offset);
}
if (offset < src.length) {
builder.append(src, offset, src.length - offset);
}
return builder.toString();
}
}@Data
public class ParameterMappingTokenHandler implements TokenHandler {
private List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = new ArrayList<ParameterMapping>();
// context是参数名称 #{id} #{username}
public String handleToken(String content) {
parameterMappings.add(buildParameterMapping(content));
return "?";
}
private ParameterMapping buildParameterMapping(String content) {
ParameterMapping parameterMapping = new ParameterMapping(content);
return parameterMapping;
}
}至此,我们的简易MyBatis框架就开发完成了。
测试
我们先来定义我们的测试类:
/**
* 框架测试类
*/
public class MybatisTest {
private SqlSession sqlSession;
private IUserDao iUserDao;
@Before
public void before() throws DocumentException, PropertyVetoException, ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
sqlSession = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build("config.xml").openSession();
iUserDao = sqlSession.getMapper(IUserDao.class);
}
/**
* 测试增删改查方法
*/
@Test
public void mybatisTest() {
UserInfo userInfo = new UserInfo();
userInfo.setUsername("测试用户名");
int row = iUserDao.insert(userInfo);
Assert.assertEquals(1, row);
UserInfo selectResult = iUserDao.selectByCondition(userInfo);
Assert.assertNotNull(selectResult);
selectResult.setUsername("测试用户名-修改");
row = iUserDao.update(selectResult);
Assert.assertEquals(1, row);
row = iUserDao.delete(selectResult);
Assert.assertEquals(1, row);
List<UserInfo> userInfos = iUserDao.selectAll();
Assert.assertEquals(0, userInfos.size());
}
@After
public void after() throws SQLException {
sqlSession.close();
}
}我们上面的测试逻辑也比较简单,就是简单的测试了我们的增删改查方法。
在这里我啰嗦一句:我们的单元测试一定要保证是可重复执行并且对数据库无污染的。也就是说我们的测试用例执行多少遍结果都是一样的,我们的测试用例执行之后对于数据库是没有污染的。
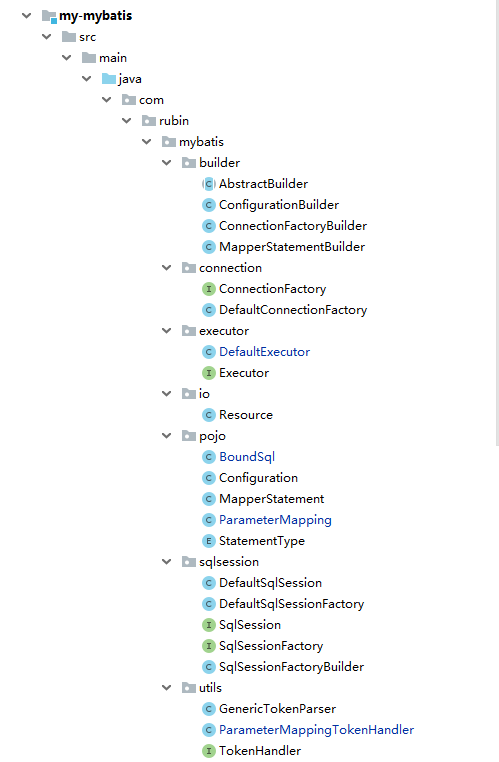
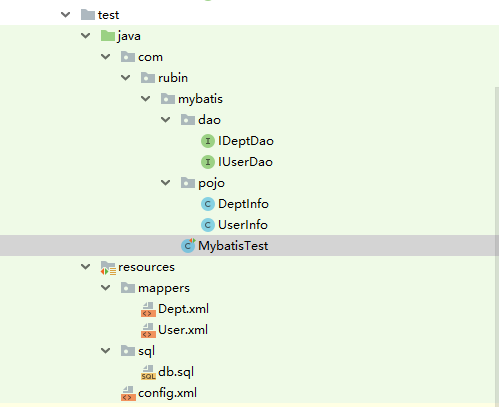
代码的目录结构如下图:
附件
源码包:my-spring-demo
文章评论
顶顶顶