Socket网络编程回顾
Socket概述
Socket就是我们常说的套接字,表示两台主机之间逻辑联结的端点。TCP/IP协议是传输层的协议,主要解决的是数据如何在网络中传输的问题。我们的Socket就是支持TCP/IP协议的网络通信基本的操作单元。它是网络通信过程中短点的抽象表示,包含进行网络通信必须的五种信息:连接使用的协议、本地主机的IP地址、本地进程的协议端口、远程主机的IP地址、远程进程的协议端口。
Socket整体流程
Socket编程主要涉及到客户端和服务端两个方面。首先是服务器创建一个服务器套接字,并把它附加到一个端口上,服务器从这个端口监听连接。端口号的范围是0-65536,但是0-1024是为特权服务保留的端口号,我们可以选择一个当前未被占用的端口进行连接监听。
客户端请求与服务器进行连接的时候,根据服务器的域名或者IP地址加上端口号,打开一个套接字连接。当服务器接受该连接之后,服务器和客户端之间就可以进行全双工的通信了。详情如下:

I/O模型
I/O模型说明
I/O模型就是指我们是用什么样的通道进行数据的发送和接收,很大程度上决定了程序通信的性能。目前Java共支持三种网编编程的I/O模型:BIO(同步并阻塞)、NIO(同步非阻塞)和AIO(异步非阻塞)。
阻塞与非阻塞是指我们访问I/O的线程是否会阻塞(或处于等待)。而同步与异步主要是指数据的请求方式,同步的话调用方会一直等待调用结果,异步指调用方不等待返回结果,而是通过回调来通知调用方。有一个给书店打电话的例子来解释上述概念比较形象,比如你打电话到书店问有没有某某书籍,书店老板说:“你等等,我找一下”,如果这时你不挂电话且不做别的事情就在一直等到老板回复你,这就是同步阻塞;如果你不挂电话,去做其他事情,过一段时间过来看看老板回复没有,这就是同步非阻塞;如果你跟老板说:“行,您有消息了给我回电。”,然后挂了电话,这就是异步非阻塞。
BIO(同步并阻塞)
Java BIO就是传统的Socket编程。
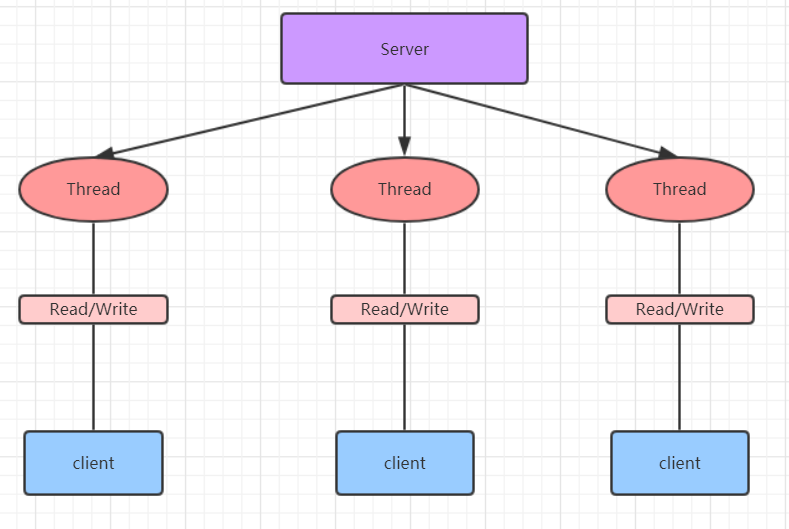
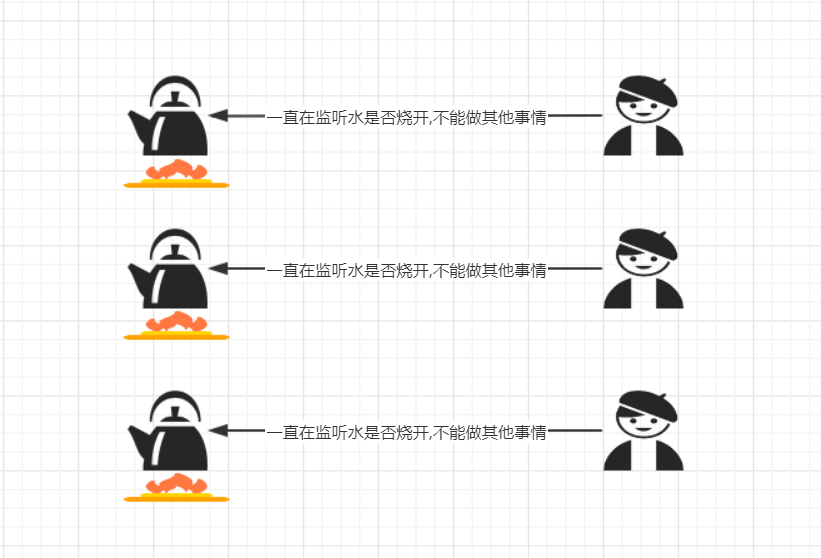
BIO(Blocking I/O):同步阻塞,服务器实现模式为一个连接一个线程,即客户端有连接请求时服务器端就需要启动一个线程去处理,如果这个连接不做任何事情会造成不必要的线程开销,我们可以通过线程池的机制去优化。
工作机制
生活示例:
问题分析
- 每个请求都需要创建独立的线程,与对应的客户端进行数据交互。
- 并发数较大时,需要创建大量线程来处理连接,系统资源占用较大。
- 连接建立后,如果当前线程暂时无数据可读,则线程阻塞在read操作上,造成资源浪费。
NIO(同步非阻塞)
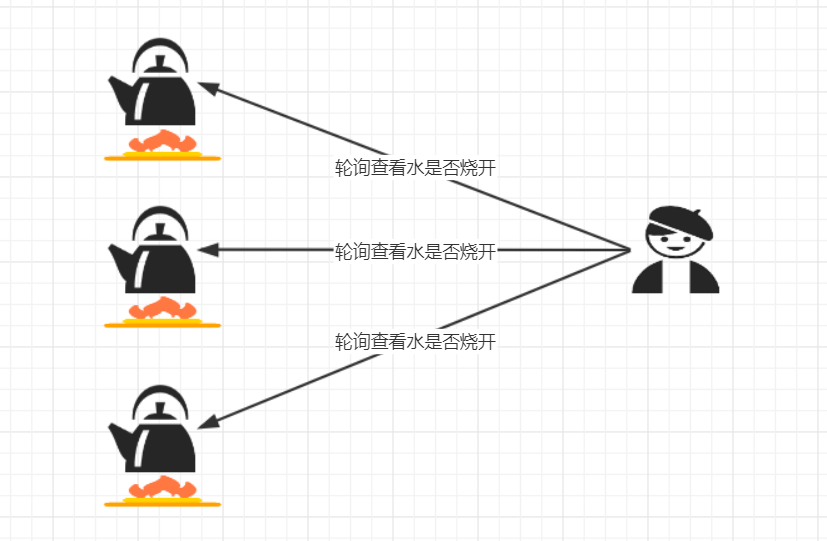
同步非阻塞,服务器实现模式为一个线程处理多个请求。即客户端发送的连接请求都会注册到多路复用器上,多路复用器轮询到连接有I/O请求就进行处理。
生活示例:
AIO(异步非阻塞)
AIO引入异步通道的概念,采用了Proactor模式,简化了程序编写,有效的请求才会启动线程去处理。它的特点是先由操作系统完成后才通知服务端程序启动线程去处理,一般适用于连接数较多且连接时间较长的应用。
Proactor模式是一个消息异步通知的设计模式,Proactor通知的不是就绪事件,而是操作完成事件。
生活示例如下:
BIO、NIO、AIO适用的场景
- BIO适用于连接数目比较小且固定的架构。这种方式对服务器的资源要求较高,并发局限在应用中,但程序简单易懂。JDK1.4之前的唯一选择。
- NIO适用于连接数目较多且连接时间较短(轻操作)的架构,比如聊天服务器,弹幕系统,服务器间通讯等。编程比较复杂,JDK1.4开始支持。
- AIO适用于连接数目多且连接比较长(重操作)的架构,比如像册服务器,充分调用OS参与并发操作,编程比较复杂,JDK7开始支持。
NIO编程
NIO介绍
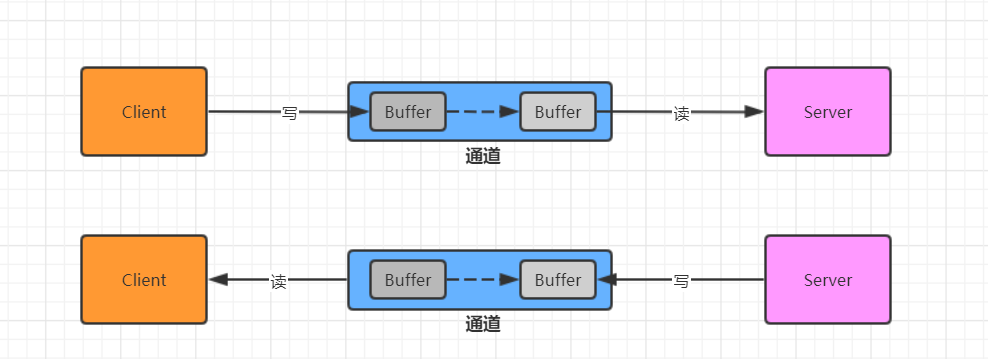
Java NIO全程Java non-blocking IO,是指JDK1.4开始提供的新的I/O的API。该API对应的I/O模型是同步非阻塞的。NIO有三大核心部分:Channel(通道)、Buffer(缓冲区)和Selector(选择器)。
NIO是面向缓冲区编程的。数据读取到一个缓冲区中,需要时可在缓冲区中前后移动,这就增加了处理过程中的灵活性。使用它可以提供非阻塞式的高伸缩性网络。
Java NIO的非阻塞模式,使一个线程从某通道发送请求或者读取数据。但是它仅能得到目前可用的数据,如果目前没有可用数据,就什么都不会获取,而不是保持线程阻塞。所以直至数据变得可以读取之前,该线程可以做其他的事情。非阻塞写也是如此,一个线程请求写入一些数据到某通道,但不需要等待它完全写入,这个线程同时可以去做别的事情。通俗理解:NIO是可以做到用一个线程来处理多个操作。假设有10000个请求过来,根据实际情况,可以分配50或者100个线程来处理。不像之前的BIO必须分配10000个线程。
NIO和BIO的比较
- BIO以流的方式处理数据,而NIO以缓冲区的方式处理数据,缓冲区的I/O效率比流要高的多
- BIO是阻塞式的,NIO是非阻塞的
- BIO的连接必须一一对应,而NIO可以一个线程处理多个操作(包括连接,读写等等)
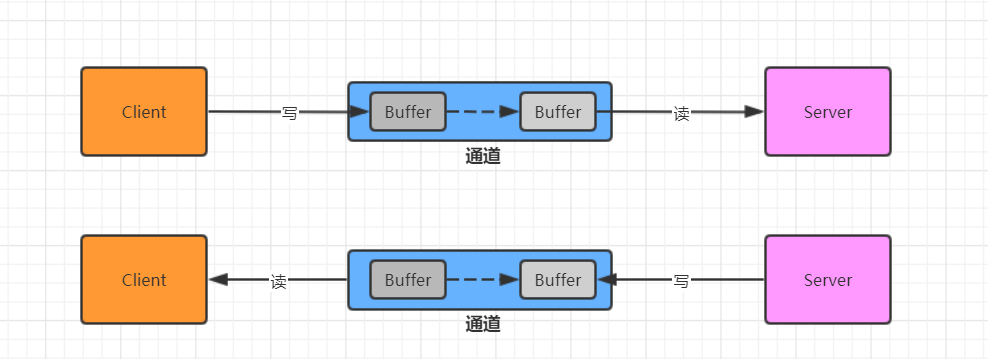
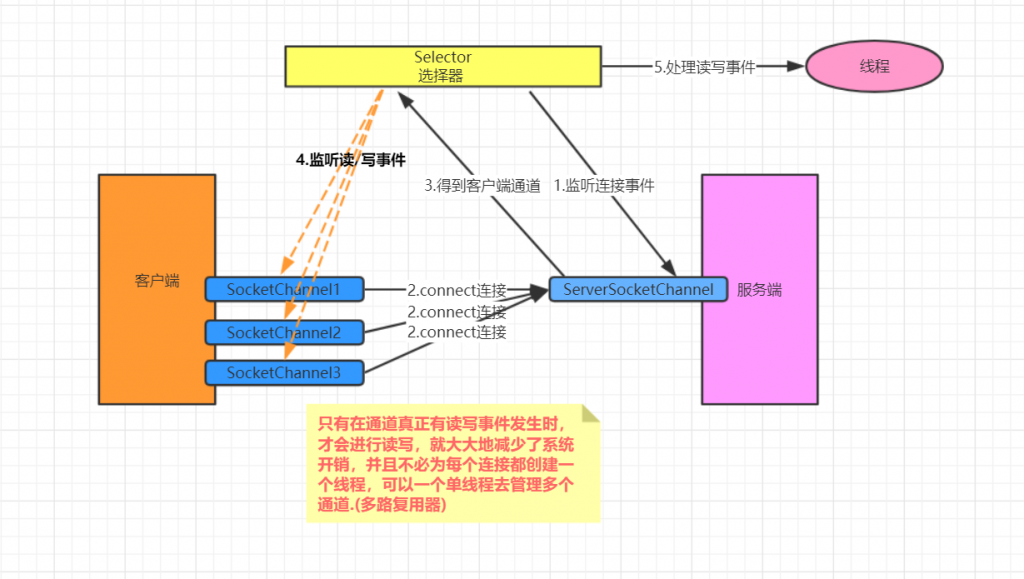
NIO三大核心原理示意图
一张图描述NIO的Selector、Channel和Buffer的关系:
- 每个Channel都会对应一个Buffer
- Selector对应一个线程,一个线程可以对应多个Channel
- 每个Channel都需要注册到Selector上
- Selector不断轮询查看Channel上的事件,时间是通道Channel非常重要的概念
- Selector会根据不用的事件,完成不同的处理操作
- Buffer就是一个内存快,底层是一个数组
- 数据的读取写入是通过Buffer这个和流不同,流只能是单向的,但是Buffer和Channel是双向的,都是支持读和写
缓冲区(Buffer)
基本介绍.
缓冲区(Buffer):本质上是一个可以读写的内存快,可以理解为一个数组。该对象提供了一组方法,可以更轻松使用内存块。缓冲区对象内置了一些机制,能够跟踪和记录缓冲区的状态变化情况。Channel提供从网络读取数据的渠道,但是读取或写入的数据必须都要经过缓冲区。
Buffer常用API介绍
Buffer及其子类如下图:
缓冲区对象的创建API如下:
| 方法名 | 说明 |
| static ByteBuffer allocate(长度) | 创建byte类型的指定长度的缓冲区 |
| static ByteBuffer wrap(byte[] array) | 创建一个有内容的byte类型的缓冲区,长度即内容长度 |
添加数据API:
| 方法名 | 说明 |
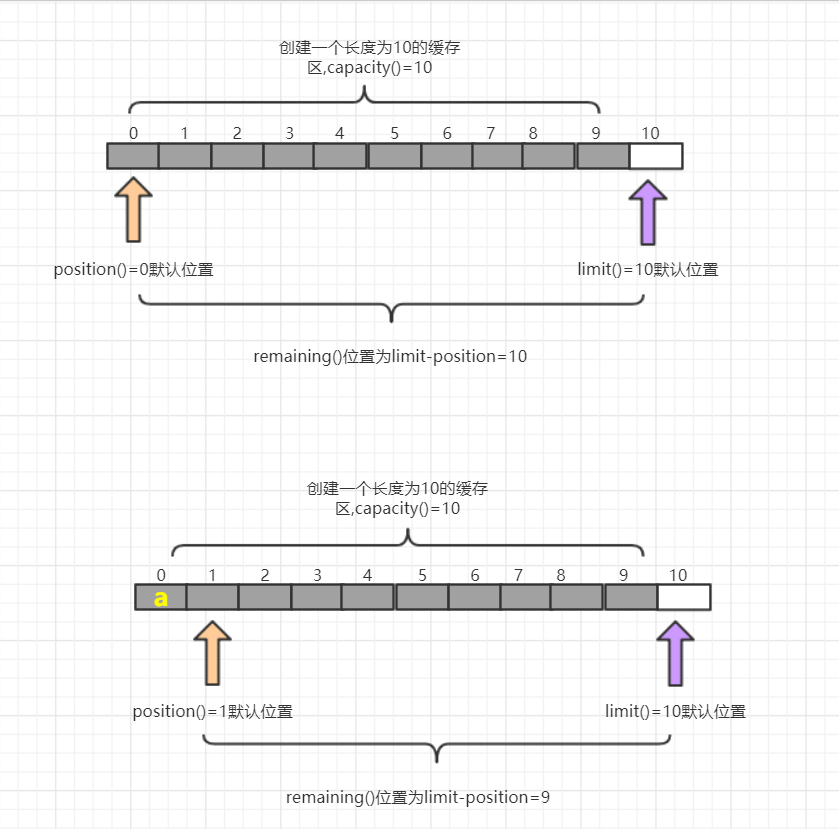
| int position()/position(int newPosition) | 获得当前要操作的索引/修改当前要操作的索引位置 |
| int limit()/limit(int newLimit) | 能最多操作到哪个索引/修改最多能操作到的索引的位置 |
| int capacity() | 返回缓冲区的总长度 |
| int remaining()/boolean hasRemaining() | 还有多少能操作索引的个数/是否还能操作 |
| put(byte b)/put(byte[] src) | 写入一个字节/写入字节数组 |
读取操作API:
| 方法名 | 介绍 |
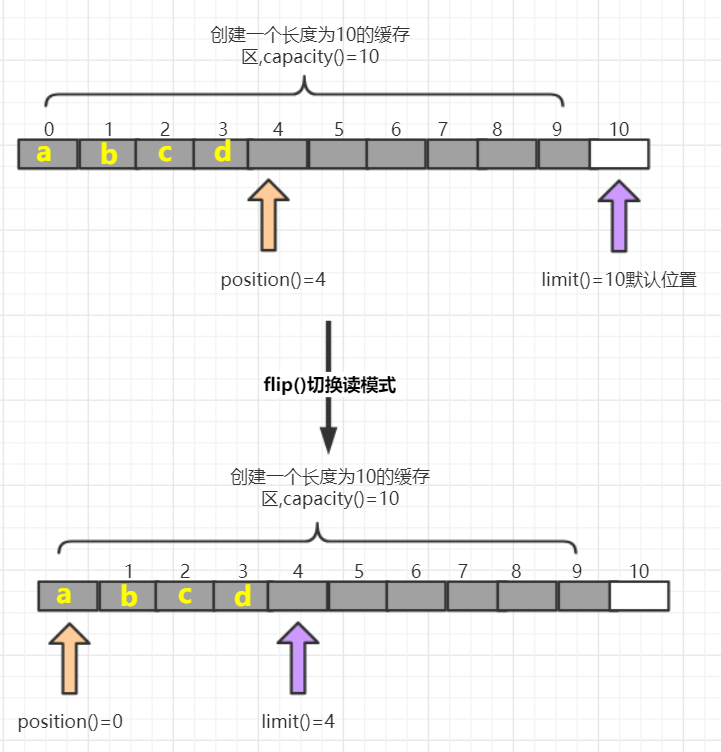
| flip() | 写切换到读模式,limit设置为position位置,position设置为0 |
| get() | 读取一个字节 |
| get(byte[] dst) | 读取多个字节 |
| get(int index) | 读指定索引的字节 |
| rewind() | 将position设置为0,可以重复读 |
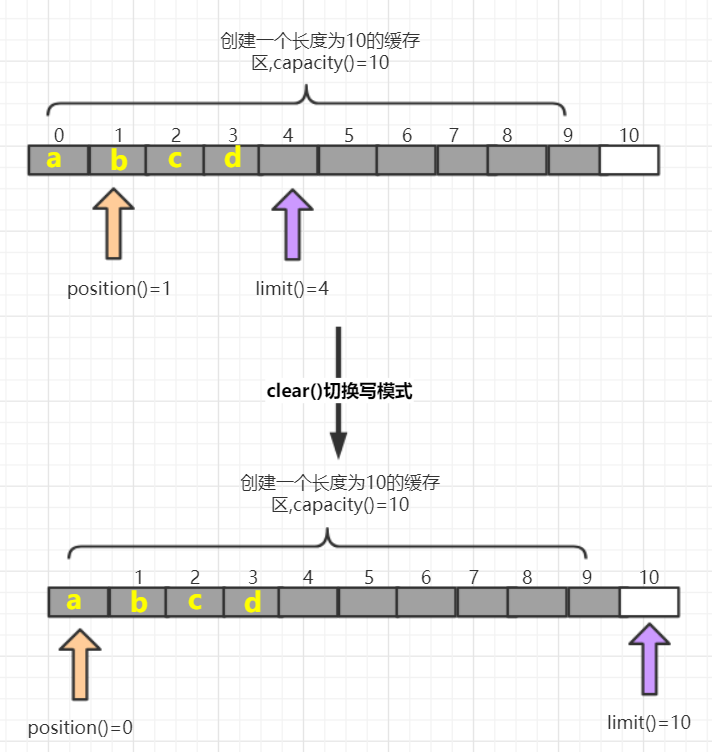
| clear() | 切换写模式,position设置为0,limit设置为capacity |
| array() | 将缓冲区转换成字节数组返回 |
flip()方法如图:
clear()方法如图:
注意事项:
- capacity:容量;limit:界限(最多能操作的位置);position:当前操作到的位置
- 获取缓冲区数据之前,需要调用flip方法
- 再次写数据之前,需要调用clear方法,但是数据还未消失,等再次写入数据,被覆盖了才会消失
通道(Channel)
基本介绍
通常来说NIO中的所有的IO都是从Channel(通道)开始的。NIO的通道类似于流,但有些区别如下:
- 通道是双向的,流是单向的
- 通道可以异步读写
- 通道总是基于缓冲区Buffer来读写
Channel常用类介绍
常用的Channel实现类有:FileChannel,DatagramChannel,ServerSocketChannel和SocketChannel,分别用于文件读写、UDP数据读写和TCP数据的读写。
Selector(选择器)
基本介绍
可以使用Selector做到用一个线程处理多个客户端连接。Selector会轮询检查注册通道的事件是否就绪并针对每个就绪的事件做相应的处理。
在没有选择器的情况下,和BIO没有区别,都是对应一个连接一个线程去处理。
添加了Selector之后,所有的就绪事件是需要一个Selector线程去处理,这样就大大的节省了资源开销。
常用API介绍
常用方法如下:
- Selector.open() : 得到一个选择器对象
- selector.select() : 阻塞 监控所有注册的通道,当有对应的事件操作时, 会将SelectionKey放入集合内部并返回事件数量
- selector.selectedKeys() : 返回存有SelectionKey的集合
SelectionKey的常用方法如下:
- SelectionKey.isAcceptable(): 是否是连接继续事件
- SelectionKey.isConnectable(): 是否是连接就绪事件
- SelectionKey.isReadable(): 是否是读就绪事件
- SelectionKey.isWritable(): 是否是写就绪事件
SelectionKey中定义的4种事件:
- SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT:接收连接继续事件,表示服务器监听到了客户连接,服务器可以接收这个连接了
- SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT:连接就绪事件,表示客户端与服务器的连接已经建立成功
- SelectionKey.OP_READ:读就绪事件,表示通道中已经有了可读的数据,可以执行读操作了(通道目前有数据,可以进行读操作了)
- SelectionKey.OP_WRITE:写就绪事件,表示已经可以向通道写数据了(通道目前可以用于写操作)
三种I/O模型的应答服务器示例
下面,我们通过三种I/O模型对应的服务器与客户端的编码示例来加深印象。
BIO
服务器示例:
/**
* bio的服务器示例
*/
@Slf4j
public class BIOServer {
private ServerSocket serverSocket;
private Integer port;
public BIOServer(Integer port) {
this.port = port;
}
/**
* 启动服务器
*/
public void start() {
try {
this.serverSocket = new ServerSocket(port);
log.info("The bio server startup success, listened on port : {}", this.port);
while (Boolean.TRUE) {
final Socket connectSocket = this.serverSocket.accept();
log.info("There is a new connection from {}:{}", connectSocket.getInetAddress().getHostAddress(), connectSocket.getPort());
new ConnectionHandler(connectSocket).start();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void close() {
if (this.serverSocket != null) {
try {
this.serverSocket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BIOServer bioServer = new BIOServer(8000);
bioServer.start();
}
}
连接处理器:
/**
* 连接处理器
*/
@AllArgsConstructor
@Slf4j
public class ConnectionHandler extends Thread {
private Socket connectSocket;
/**
* 处理连接
*/
@Override
public void run() {
super.run();
try (
final InputStream inputStream = this.connectSocket.getInputStream();
final OutputStream outputStream = this.connectSocket.getOutputStream()
) {
while (Boolean.TRUE) {
final String receiveMsg = IOUtil.readLine(inputStream);
log.info("Receive msg from {}:{}, the msg content is {}", connectSocket.getInetAddress().getHostAddress(), connectSocket.getPort(), receiveMsg);
String responseMsg = "From server:";
if ("quit".equalsIgnoreCase(receiveMsg)) {
responseMsg += "Bye Bye";
} else {
responseMsg += receiveMsg;
}
IOUtil.writeLine(responseMsg, outputStream);
if ("quit".equalsIgnoreCase(receiveMsg)) {
break;
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
log.info("The Client {}:{} is offline", connectSocket.getInetAddress().getHostAddress(), connectSocket.getPort());
close();
}
}
/**
* 释放资源
*/
private void close() {
if (this.connectSocket != null) {
try {
this.connectSocket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}工具类:
/**
* 工具类
*/
public class IOUtil {
/**
* 读取一行数据
*
* @param inputStream
* @return
* @throws IOException
*/
public static String readLine(InputStream inputStream) throws IOException {
byte[] bytes = new byte[1];
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(102400);
while (inputStream.read(bytes) != -1) {
String charStr = new String(bytes);
if ("\n".equalsIgnoreCase(charStr)) {
break;
}
byteBuffer.put(bytes);
}
return new String(byteBuffer.array(), 0, byteBuffer.position(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
}
/**
* 写一行数据
*
* @param msg
* @param outputStream
* @throws IOException
*/
public static void writeLine(String msg, OutputStream outputStream) throws IOException {
if (!msg.endsWith("\n")) {
msg += "\n";
}
outputStream.write(msg.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
outputStream.flush();
}
}
客户端:
@Slf4j
public class BIOClient {
private Socket socket;
private Integer port;
public BIOClient(Integer port) {
this.port = port;
}
/**
* 开始连接并处理业务
*/
public void start() {
try {
this.socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", this.port);
log.info("Connect to 127.0.0.1:{} with 127.0.0.1:{}", this.port, this.socket.getLocalPort());
final InputStream inputStream = this.socket.getInputStream();
final OutputStream outputStream = this.socket.getOutputStream();
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
while (Boolean.TRUE) {
final String inputMsg = reader.readLine();
IOUtil.writeLine(inputMsg, outputStream);
final String responseMsg = IOUtil.readLine(inputStream);
log.info("{}", responseMsg);
if ("quit".equalsIgnoreCase(inputMsg)) {
break;
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
close();
}
}
/**
* 释放资源
*/
private void close() {
if (this.socket != null) {
try {
this.socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BIOClient bioClient = new BIOClient(8000);
bioClient.start();
}
}这里需要注意的是对于流读取的结尾应该自定义特殊字符,实例中使用的换行符为结束符并通过ByteBuffer来作中转来处理中文编码问题。
这些编码对于新手比较容易遇到的坑是服务器接受连接之后阻塞读取客户端的数据,如果此时使用inputstream.read() != -1作为读取结束条件的话,会一直阻塞到此处,直到客户端断开连接(因为在非断开连接的情况下永远不可能读取返回-1)。所以,我们在使用BIO编码的时候,可以采用自定义协议(前几位标识出此条消息的长度等等)或者自定义结束符的方式来解决此问题。
NIO
服务器:
/**
* NIO服务器
*/
@Slf4j
public class NIOServer {
private Selector selector;
private ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel;
private Integer port;
public NIOServer(Integer port) {
this.port = port;
}
/**
* 启动服务器并处理业务
*/
public void start() {
try {
this.selector = Selector.open();
this.serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
this.serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", this.port));
this.serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(Boolean.FALSE);
this.serverSocketChannel.register(this.selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
log.info("The nio server startup success, listened on port : {}", this.port);
while (Boolean.TRUE) {
final int select = this.selector.select(2000);
if (select == 0) {
continue;
}
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = this.selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey selectionKey = iterator.next();
if (selectionKey.isAcceptable()) {
// 处理新连接
handleNewConnection(selectionKey);
} else if (selectionKey.isReadable()) {
// 处理读就绪事件 即客户端发送消息过来
handleNewMessage(selectionKey);
}
// 从集合中删除对应的key 避免重复处理
iterator.remove();
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 释放资源
*/
public void close() {
if (this.selector != null) {
try {
this.selector.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (this.serverSocketChannel != null) {
try {
this.serverSocketChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 处理新客户端连接
*
* @param selectionKey
*/
private void handleNewConnection(SelectionKey selectionKey) throws IOException {
SocketChannel socketChannel = this.serverSocketChannel.accept();
log.info("There is a new connection from {}", socketChannel.getRemoteAddress());
socketChannel.configureBlocking(Boolean.FALSE);
socketChannel.register(this.selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
/**
* 处理读就绪事件
*
* @param selectionKey
*/
private void handleNewMessage(SelectionKey selectionKey) throws IOException {
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(102400);
int read = socketChannel.read(byteBuffer);
if (read > 0) {
String receiveMsg = new String(byteBuffer.array(), 0, byteBuffer.position(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
log.info("Receive msg from {}, the msg content is {}", socketChannel.getRemoteAddress(), receiveMsg);
String responseMsg = "From server:";
if ("quit".equalsIgnoreCase(receiveMsg)) {
responseMsg += "Bye Bye";
} else {
responseMsg += receiveMsg;
}
socketChannel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap(responseMsg.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)));
if ("quit".equalsIgnoreCase(receiveMsg)) {
log.info("The Client {} is offline", socketChannel.getRemoteAddress());
socketChannel.close();
selectionKey.cancel();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
NIOServer nioServer = new NIOServer(9000);
nioServer.start();
}
}
客户端:
/**
* NIO客户端
*/
@Slf4j
public class NIOClient {
private SocketChannel socketChannel;
private Integer port;
public NIOClient(Integer port) {
this.port = port;
}
public void start() {
try {
this.socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
this.socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", this.port));
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(102400);
log.info("Connect to 127.0.0.1:{} with {}", this.port, this.socketChannel.getLocalAddress());
while (Boolean.TRUE) {
String inputMsg = reader.readLine();
this.socketChannel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap(inputMsg.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)));
byteBuffer.clear();
int read = this.socketChannel.read(byteBuffer);
if (read > 0) {
String responseMsg = new String(byteBuffer.array(), 0, byteBuffer.position(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
log.info("{}", responseMsg);
if ("quit".equalsIgnoreCase(inputMsg)) {
break;
}
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
close();
}
}
/**
* 释放资源
*/
private void close() {
if (this.socketChannel != null) {
try {
this.socketChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
NIOClient nioClient = new NIOClient(9000);
nioClient.start();
}
}
AIO
服务器:
/**
* AIO服务器
*/
@Data
@Slf4j
public class AIOServer {
private AsynchronousServerSocketChannel asynchronousServerSocketChannel;
private Integer port;
private CountDownLatch countDownLatch;
public AIOServer(Integer port) {
this.port = port;
}
/**
* 启动服务器
*/
public void start() {
try {
this.countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(1);
this.asynchronousServerSocketChannel = AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.open();
this.asynchronousServerSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", this.port));
log.info("The aio server startup success, listened on port : {}", this.port);
this.asynchronousServerSocketChannel.accept(this, new ConnectionCompletionHandler());
this.countDownLatch.await();
this.asynchronousServerSocketChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 关闭服务器
*/
public void close() {
if (this.countDownLatch != null) {
long count = this.countDownLatch.getCount();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
this.countDownLatch.countDown();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AIOServer aioServer = new AIOServer(10000);
aioServer.start();
}
}连接完成回调处理器:
@Slf4j
public class ConnectionCompletionHandler implements CompletionHandler<AsynchronousSocketChannel, AIOServer> {
/**
* Invoked when an operation has completed.
*
* @param result The result of the I/O operation.
* @param attachment
*/
@Override
public void completed(AsynchronousSocketChannel result, AIOServer attachment) {
// 继续监听连接
attachment.getAsynchronousServerSocketChannel().accept(attachment, this);
// 新建立的连接建立读事件完成
try {
log.info("There is a new connection from {}", result.getRemoteAddress());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(102400);
result.read(byteBuffer, byteBuffer, new ReadCompletionHandler(result));
}
/**
* Invoked when an operation fails.
*
* @param exc The exception to indicate why the I/O operation failed
* @param attachment
*/
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, AIOServer attachment) {
log.info("There is a new connection failed cause {}", exc);
}
}
读取完成回调处理器:
@Slf4j
public class ReadCompletionHandler implements CompletionHandler<Integer, ByteBuffer> {
private AsynchronousSocketChannel asynchronousSocketChannel;
public ReadCompletionHandler(AsynchronousSocketChannel asynchronousSocketChannel) {
this.asynchronousSocketChannel = asynchronousSocketChannel;
}
/**
* Invoked when an operation has completed.
*
* @param result The result of the I/O operation.
* @param attachment
*/
@Override
public void completed(Integer result, ByteBuffer attachment) {
// 切换成读模式
attachment.flip();
// 读取客户端内容
String receiveMsg = new String(attachment.array(), 0, attachment.limit(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
try {
log.info("Receive msg from {}, the msg content is {}", this.asynchronousSocketChannel.getRemoteAddress(), receiveMsg);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 做出服务器响应
doResponse(receiveMsg);
attachment.clear();
try {
this.asynchronousSocketChannel.read(attachment, attachment, this);
} catch (Exception e){
close();
}
}
private void doResponse(String receiveMsg) {
String responseMsg = "From server:";
if ("quit".equalsIgnoreCase(receiveMsg)) {
responseMsg += "Bye Bye";
} else {
responseMsg += receiveMsg;
}
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(responseMsg.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
this.asynchronousSocketChannel.write(byteBuffer, byteBuffer, new CompletionHandler<Integer, ByteBuffer>() {
@Override
public void completed(Integer result, ByteBuffer attachment) {
// 如果一次没有写完 继续写
if (attachment.hasRemaining()) {
ReadCompletionHandler.this.asynchronousSocketChannel.write(attachment, attachment, this);
} else {
if ("quit".equalsIgnoreCase(receiveMsg)) {
try {
log.info("The Client {} is offline", ReadCompletionHandler.this.asynchronousSocketChannel.getRemoteAddress());
close();
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
}
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, ByteBuffer attachment) {
close();
}
});
}
/**
* Invoked when an operation fails.
*
* @param exc The exception to indicate why the I/O operation failed
* @param attachment
*/
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, ByteBuffer attachment) {
close();
}
/**
* 关闭连接
*/
private void close() {
if (this.asynchronousSocketChannel != null) {
try {
this.asynchronousSocketChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}客户端:
/**
* AIO客户端
*/
@Data
@Slf4j
public class AIOClient {
private AsynchronousSocketChannel asynchronousSocketChannel;
private Integer port;
private CountDownLatch countDownLatch;
public AIOClient(Integer port) {
this.port = port;
}
public void start() {
try {
this.countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(1);
this.asynchronousSocketChannel = AsynchronousSocketChannel.open();
this.asynchronousSocketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", this.port), this, new ClientConnectionCompletionHandler(this));
countDownLatch.await();
this.asynchronousSocketChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 关闭客户端
*/
public void close() {
if (this.countDownLatch != null) {
long count = this.countDownLatch.getCount();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
this.countDownLatch.countDown();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AIOClient aioClient = new AIOClient(10000);
aioClient.start();
}
}客户端连接成功处理器:
/**
* 连接完成处理类
*/
@Slf4j
@AllArgsConstructor
public class ClientConnectionCompletionHandler implements CompletionHandler<Void, AIOClient> {
private AIOClient aioClient;
/**
* Invoked when an operation has completed.
*
* @param result The result of the I/O operation.
* @param attachment
*/
@Override
public void completed(Void result, AIOClient attachment) {
try {
log.info("Connect to {} with {}", attachment.getAsynchronousSocketChannel().getRemoteAddress(), attachment.getAsynchronousSocketChannel().getLocalAddress());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String consoleMsg = "";
try {
consoleMsg = reader.readLine();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(consoleMsg.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
this.aioClient.getAsynchronousSocketChannel().write(byteBuffer, byteBuffer, new CompletionHandler<Integer, ByteBuffer>() {
@Override
public void completed(Integer result, ByteBuffer attachment) {
if (attachment.hasRemaining()) {
ClientConnectionCompletionHandler.this.aioClient.getAsynchronousSocketChannel().write(attachment, attachment, this);
} else {
ByteBuffer readBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(102400);
ClientConnectionCompletionHandler.this.aioClient.getAsynchronousSocketChannel().read(readBuffer, readBuffer, new CompletionHandler<Integer, ByteBuffer>() {
@Override
public void completed(Integer result, ByteBuffer attachment) {
// 切换读模式
attachment.flip();
String responseMsg = new String(attachment.array(), 0, attachment.limit(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
log.info("{}", responseMsg);
if ("From Server:Bye Bye".equalsIgnoreCase(responseMsg)) {
ClientConnectionCompletionHandler.this.aioClient.close();
}
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, ByteBuffer attachment) {
exc.printStackTrace();
}
});
String consoleMsg = "";
try {
consoleMsg = reader.readLine();
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(consoleMsg.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
ClientConnectionCompletionHandler.this.aioClient.getAsynchronousSocketChannel().write(byteBuffer, byteBuffer, this);
}
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, ByteBuffer attachment) {
}
});
}
/**
* Invoked when an operation fails.
*
* @param exc The exception to indicate why the I/O operation failed
* @param attachment
*/
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, AIOClient attachment) {
exc.printStackTrace();
}
}写在最后
网络编程在我们在我们的工作生活中还是很重要的,我们想要了解HTTP、上传下载、聊天室等等常用功能的底层实现的话,网络编程是我们必须要掌握的知识。
上述示例是我调试好并且认为很好的入门案例,有兴趣的小伙伴可以细细研究一下。有问题欢迎留言交流~~






文章评论