Stream解决的痛点问题
MQ消息中间件广泛应用在应用解耦合、异步消息处理、流量削峰等场景中。不同的MQ消息中间件机制包括使用方式会有所不同。比如RabbitMQ中有Exchange(交换机/交换器)这一概念,Kafka有Topic、Partition分区这些概念。MQ消息中间件的差异性不利于我们上层的开发应用,当我们系统希望从原来的RabbitMQ切换到Kafka时,就会比较困难了,因为此时应用程序和具体某款MQ消息中间件已经耦合在一起了。
SpringCloud Stream进行了很好的上层抽象,可以让我们与具体的消息中间件解耦,屏蔽掉底层具体MQ的细节差异。如此一来,我们的学习、开发、维护MQ都会变得轻松。
目前SpringCloud Stream支持RabbitMQ和kafka。
Stream重要概念
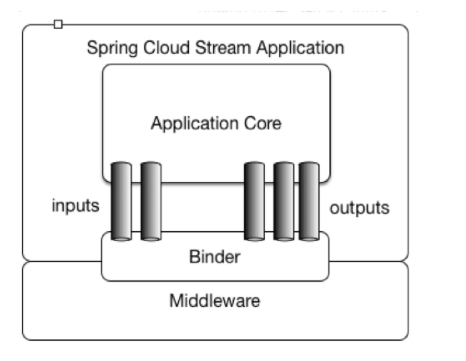
Spring Cloud Stream是一个构建消息驱动微服务的框架。应用程序通过Inputs(相当于消息消费者Consumer)或者Outputs(相当于消息生产者Producer)来与SpringCloud Stream中的binder对象交互,而binder对象是用来屏蔽底层MQ细节的,它负责与具体的消息中间件交互。
Stream消息通信方式及编程模型
Stream消息通信方式
在Spring Cloud Stream中的消息通信方式遵循了发布-订阅模式,当⼀条消息被投递到消息中间件之后,它会通过共享的Topic主题进行广播,消息消费者在订阅的主题中收到它并触发自身的业务逻辑处理。这里所提到的Topic主题是SpringCloud Stream中的⼀个抽象概念,用来代表发布共享消息给消费者的地方。在不同的消息中间件中,Topic可能对应着不同的概念,比如:在RabbitMQ中的它对应了Exchange、在Kakfa中则对应了Kafka中的Topic。
Stream编程注解
| 注解 | 描述 |
| @Input(在消费者工程中使用) | 注解标识输入通道,通过该输入通道接收到的消息进入应用程序 |
| @Output(在生产者工程中适用) | 注解标识输出通道,发布的消息将通过该通道离开应用程序 |
| @StreamListener(在消费者工程中使用,监听message的到来) | 监听队列,用于消费者的队列的消息的接收(有消息监听......) |
| @EnableBinding | 把Channel和Exchange(对于RabbitMQ)绑定在一起 |
Stream应用
我们下面的消息模块的定义是在博文SpringCloud Netflix之Eureka Server中搭建的大框架下创建的,有需要的可以参考该博文的大框架的搭建。
我们在spring-cloud-demo模块下创建消息模块stream,其pom文件如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-demo</artifactId>
<groupId>com.rubin</groupId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>stream</artifactId>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-stream-rabbit</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-config-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-bus-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>启动类如下:
package com.rubin.stream;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
public class StreamBootstrap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(StreamBootstrap.class);
}
}
配置文件如下:
bootstrap.yml:
spring:
profiles:
active: eurekabootstrap-eureka.yml:
spring:
cloud:
config:
name: stream
profile: eureka
label: master
uri: http://config-server-host:9400在配置仓库新建stream的文件夹并上传stream-eureka.yml文件,文件内容为:
server:
port: 9300
spring:
application:
name: stream
rabbitmq:
host: rabbitmq-host
port: 5672
username: root
password: 123456
cloud:
stream:
# 绑定MQ服务信息(此处我们是RabbitMQ)
binders:
# 给Binder定义的名称,用于后面的关联
rubinBinder:
# MQ类型,如果是Kafka的话,此处配置kafka
type: rabbit
# MQ环境配置(用户名、密码等)
environment:
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: rabbitmq-host
port: 5672
username: root
password: 123456
# 关联整合通道和binder对象
bindings:
# output是我们定义的通道名称,此处不能乱改
output:
# 要使用的Exchange名称(消息队列主题名称)
destination: rubinExchange
# application/json # 消息类型设置,比如json
content-type: text/plain
# 关联MQ服务
binder: rubinBinder
input:
# 要使用的Exchange名称(消息队列主题名称)
destination: rubinExchange
# application/json # 消息类型设置,比如json
content-type: text/plain
# 关联MQ服务
binder: rubinBinder
group: rubinGroup1
eureka:
instance:
hostname: 127.0.0.1
prefer-ip-address: true
# 配置中心读取的配置不能解析@。。@来标注的pom文件中的变量,只能写死或者配置在该配置文件中用${}的形式引用
instance-id: ${spring.cloud.client.ip-address}:${spring.application.name}:${server.port}:1.0-SNAPSHOT
# 租约续约间隔时间,默认30秒
lease-renewal-interval-in-seconds: 30
# 租约到期,服务时效时间,默认值90秒,服务超过90秒没有发生心跳,EurekaServer会将服务从列表移除
lease-expiration-duration-in-seconds: 90
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://eureka-host:8761/eureka/,http://eureka-host:8762/eureka/
register-with-eureka: true
# 每隔多久拉取一次服务列表
registry-fetch-interval-seconds: 30
fetch-registry: true
# 配制了该项 回阻止将该实例注册为一个eureka client 默认是true 默认自动加入一个Maker类标记 所以引入eureka-client依赖之后 加不加@EnableEurekaClient都会默认注册进EurekaServer
# enabled: false
# springboot中暴露健康检查等断点接口
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: "*"
# 暴露健康接口的细节
endpoint:
health:
show-details: always如果不使用配置中心可以把上面的配置直接拷贝到项目中。
我们开发一个消息发送接口如下:
package com.rubin.stream.producer;
public interface IMessageProducer {
/**
* 向mq中发送消息(并不是直接操作mq,应该操作的是spring cloud stream)
* 使用通道向外发出消息(指的是Source里面的output通道)
*
* @param content
*/
void sendMessage(String content);
}
开发我们的消息发送者逻辑:
package com.rubin.stream.producer;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cloud.stream.annotation.EnableBinding;
import org.springframework.cloud.stream.messaging.Source;
import org.springframework.messaging.support.MessageBuilder;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
// Source.class里面就是对输出通道的定义(这是Spring Cloud Stream内置的通道封装)
@EnableBinding(Source.class)
// 没必要必须加该注解 此处加上的意义是区分多个生产者
@Component(value = "defaultMessageProducerImpl")
public class DefaultMessageProducerImpl implements IMessageProducer {
// 将MessageChannel的封装对象Source注⼊到这里使用
@Autowired
private Source source;
/**
* 向mq中发送消息(并不是直接操作mq,应该操作的是spring cloud stream)
* 使用通道向外发出消息(指的是Source⾥⾯的output通道)
*
* @param content
*/
@Override
public void sendMessage(String content) {
source.output().send(MessageBuilder.withPayload(content).build());
}
}
开发消息发送实体:
package com.rubin.stream.po;
import lombok.Data;
import java.io.Serializable;
@Data
public class SendMessagePO implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -2326072132441433242L;
private String content;
}
开发消息发送Controller:
package com.rubin.stream.controller;
import com.rubin.stream.po.SendMessagePO;
import com.rubin.stream.producer.IMessageProducer;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("message")
public class MessageController {
@Autowired
@Qualifier(value = "defaultMessageProducerImpl")
private IMessageProducer defaultMessageProducer;
@PostMapping("default/send")
public String sendDefaultMessage(@RequestBody SendMessagePO sendMessagePO) {
defaultMessageProducer.sendMessage(sendMessagePO.getContent());
return "发送成功";
}
}
至此,我们的消息发送逻辑就写完了。接下来写我们的消息消费逻辑。
定义我们的消费者监听类:
package com.rubin.stream.consumer;
import org.springframework.cloud.stream.annotation.EnableBinding;
import org.springframework.cloud.stream.annotation.StreamListener;
import org.springframework.cloud.stream.messaging.Sink;
import org.springframework.messaging.Message;
@EnableBinding(Sink.class)
public class DefaultConsumer {
@StreamListener(Sink.INPUT)
public void recevieMessages(Message<String> message) {
System.out.println("DefaultConsumer=========接收到的消息:" + message);
}
}
正常来讲,我们的服务的消息消费和消息生产都是分开写的。但是也不排除一个服务是两种身份的情况,所以我们用一个服务担任了两种角色。我们在生产中可以根据角色做相应的调整即可。
开发完成之后,启动服务。我们发送http://127.0.0.1:9300/message/default/send的POST请求来测试,请求参数为:
{
"content": "测试默认消息"
}正常我们发送消息之后,控制台会打印消费消息的日志。
Stream高级之自定义消息通道
Stream内置了两种接口Source和Sink分别定义了 Binding 为 “input” 的输⼊流和“output” 的输出流,我们也可以自定义各种输入输出流(通道)。但实际我们可以在我们的服务中使用多个binder、多个输入通道和输出通道,然而默认就带了⼀个input的输入通道和⼀个output的输出通道,怎么办?
我们是可以自定义消息通道的,学着Source和Sink的样子,给你的通道定义个自己的名字,多个输入通道和输出通道是可以写在⼀个类中的。示例如下:
package com.rubin.stream.channel;
import org.springframework.cloud.stream.annotation.Input;
import org.springframework.cloud.stream.annotation.Output;
import org.springframework.messaging.MessageChannel;
import org.springframework.messaging.SubscribableChannel;
public interface RubinChannel {
String RUBIN_INPUT = "rubinInput";
String RUBIN_OUTPUT = "rubinOutput";
@Input(RUBIN_INPUT)
SubscribableChannel rubinInput();
@Output(RUBIN_OUTPUT)
MessageChannel rubinOutput();
}
修改配置文件为:
server:
port: 9300
spring:
application:
name: stream
rabbitmq:
host: rabbitmq-host
port: 5672
username: root
password: 123456
cloud:
stream:
# 绑定MQ服务信息(此处我们是RabbitMQ)
binders:
# 给Binder定义的名称,用于后面的关联
rubinBinder:
# MQ类型,如果是Kafka的话,此处配置kafka
type: rabbit
# MQ环境配置(用户名、密码等)
environment:
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: rabbitmq-host
port: 5672
username: root
password: 123456
# 关联整合通道和binder对象
bindings:
# output是我们定义的通道名称,此处不能乱改
output:
# 要使用的Exchange名称(消息队列主题名称)
destination: rubinExchange
# application/json # 消息类型设置,比如json
content-type: text/plain
# 关联MQ服务
binder: rubinBinder
rubinOutput:
# 要使用的Exchange名称(消息队列主题名称)
destination: rubinExchange
# application/json # 消息类型设置,比如json
content-type: text/plain
# 关联MQ服务
binder: rubinBinder
input:
# 要使用的Exchange名称(消息队列主题名称)
destination: rubinExchange
# application/json # 消息类型设置,比如json
content-type: text/plain
# 关联MQ服务
binder: rubinBinder
group: rubinGroup1
rubinInput:
# 要使用的Exchange名称(消息队列主题名称)
destination: rubinExchange
# application/json # 消息类型设置,比如json
content-type: text/plain
# 关联MQ服务
binder: rubinBinder
group: rubinGroup2
eureka:
instance:
hostname: 127.0.0.1
prefer-ip-address: true
# 配置中心读取的配置不能解析@。。@来标注的pom文件中的变量,只能写死或者配置在该配置文件中用${}的形式引用
instance-id: ${spring.cloud.client.ip-address}:${spring.application.name}:${server.port}:1.0-SNAPSHOT
# 租约续约间隔时间,默认30秒
lease-renewal-interval-in-seconds: 30
# 租约到期,服务时效时间,默认值90秒,服务超过90秒没有发生心跳,EurekaServer会将服务从列表移除
lease-expiration-duration-in-seconds: 90
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://eureka-host:8761/eureka/,http://eureka-host:8762/eureka/
register-with-eureka: true
# 每隔多久拉取一次服务列表
registry-fetch-interval-seconds: 30
fetch-registry: true
# 配制了该项 回阻止将该实例注册为一个eureka client 默认是true 默认自动加入一个Maker类标记 所以引入eureka-client依赖之后 加不加@EnableEurekaClient都会默认注册进EurekaServer
# enabled: false
# springboot中暴露健康检查等断点接口
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: "*"
# 暴露健康接口的细节
endpoint:
health:
show-details: always新增自定义通道生产者:
package com.rubin.stream.producer;
import com.rubin.stream.channel.RubinChannel;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cloud.stream.annotation.EnableBinding;
import org.springframework.messaging.support.MessageBuilder;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@EnableBinding(RubinChannel.class)
@Component(value = "rubinMessageProducerImpl")
public class RubinMessageProducerImpl implements IMessageProducer {
@Autowired
private RubinChannel rubinChannel;
/**
* 向mq中发送消息(并不是直接操作mq,应该操作的是spring cloud stream)
* 使用通道向外发出消息(指的是Source里面的output通道)
*
* @param content
*/
@Override
public void sendMessage(String content) {
rubinChannel.rubinOutput().send(MessageBuilder.withPayload(content).build());
}
}
自定义通道消费者:
package com.rubin.stream.consumer;
import com.rubin.stream.channel.RubinChannel;
import org.springframework.cloud.stream.annotation.EnableBinding;
import org.springframework.cloud.stream.annotation.StreamListener;
import org.springframework.cloud.stream.messaging.Sink;
import org.springframework.messaging.Message;
@EnableBinding(RubinChannel.class)
public class RubinConsumer {
@StreamListener(RubinChannel.RUBIN_INPUT)
public void recevieMessages(Message<String> message) {
System.out.println("RubinConsumer=========接收到的消息:" + message);
}
}
Controller修改如下:
package com.rubin.stream.controller;
import com.rubin.stream.po.SendMessagePO;
import com.rubin.stream.producer.IMessageProducer;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("message")
public class MessageController {
@Autowired
@Qualifier(value = "defaultMessageProducerImpl")
private IMessageProducer defaultMessageProducer;
@Autowired
@Qualifier(value = "rubinMessageProducerImpl")
private IMessageProducer rubinMessageProducer;
@PostMapping("default/send")
public String sendDefaultMessage(@RequestBody SendMessagePO sendMessagePO) {
defaultMessageProducer.sendMessage(sendMessagePO.getContent());
return "发送成功";
}
@PostMapping("rubin/send")
public String sendRubinMessage(@RequestBody SendMessagePO sendMessagePO) {
rubinMessageProducer.sendMessage(sendMessagePO.getContent());
return "发送成功";
}
}
启动服务发起调用。我们会发现使用那个通道发送消息两个消费者均可正常消费消息。
Stream高级之消息分组
如上我们的情况,消费者端有两个(消费同⼀个MQ的同⼀个主题)。但是呢,我们的业务场景中希望这个主题的⼀个message只能被⼀个消费者端消费处理,此时我们就可以使用消息分组。
我们仅仅需要在服务消费者端设置 spring.cloud.stream.bindings.input.group 属性,多个消费者实例配置为同⼀个group名称(在同⼀个group中的多个消费者只有⼀个可以获取到消息并消费)。
以上就是博文全部内容。欢迎小伙伴们积极留言交流~~~

文章评论