数据脱敏是指对某些敏感信息通过脱敏规则进行数据的变形,实现敏感隐私数据的可靠保护。涉及客户安全数据或者一些商业性敏感数据,如身份证号、手机号、卡号、客户号等个人信息按照规定,都需要进行数据脱敏。
数据脱敏模块属于ShardingSphere分布式治理这一核心功能下的子功能模块。
- 在更新操作时,它通过对用户输入的SQL进行解析,并依据用户提供的脱敏配置对SQL进行改写,从而实现对原文数据进行加密,并将密文数据存储到底层数据库
- 在查询数据时,它又从数据库中取出密文数据,并对其解密,最终将解密后的原始数据返回给用户
Apache ShardingSphere自动化&透明化了数据脱敏过程,让用户无需关注数据脱敏的实现细节,像使用普通数据那样使用脱敏数据。
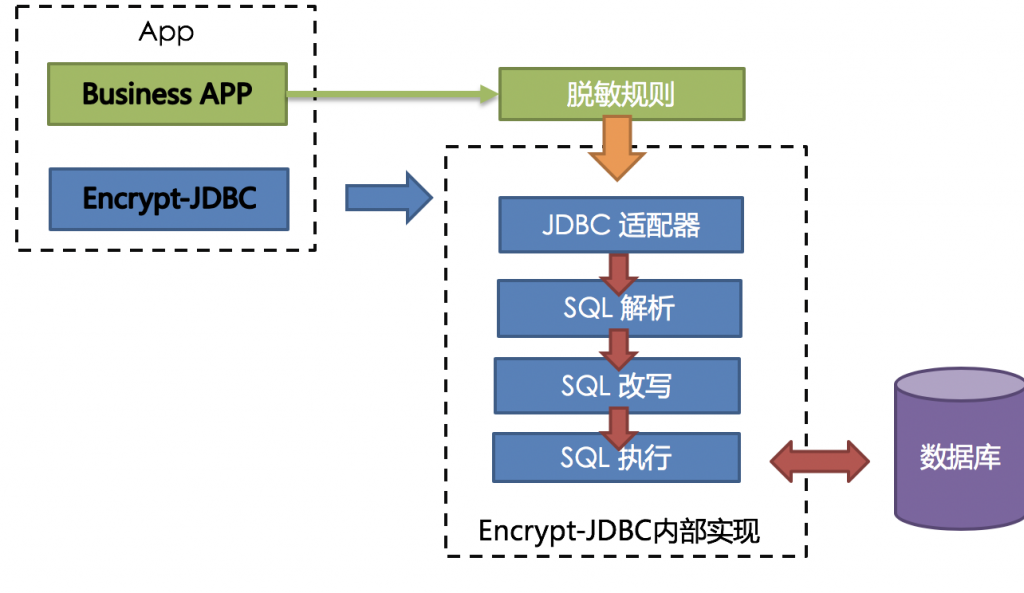
整体架构
ShardingSphere提供的Encrypt-JDBC和业务代码部署在一起。业务方需面向Encrypt-JDBC进行JDBC编程。
Encrypt-JDBC将用户发起的SQL进行拦截,并通过SQL语法解析器进行解析、理解SQL行为,再依据用户传入的脱敏规则,找出需要脱敏的字段和所使用的加解密器对目标字段进行加解密处理后,再与底层数据库进行交互。
脱敏规则
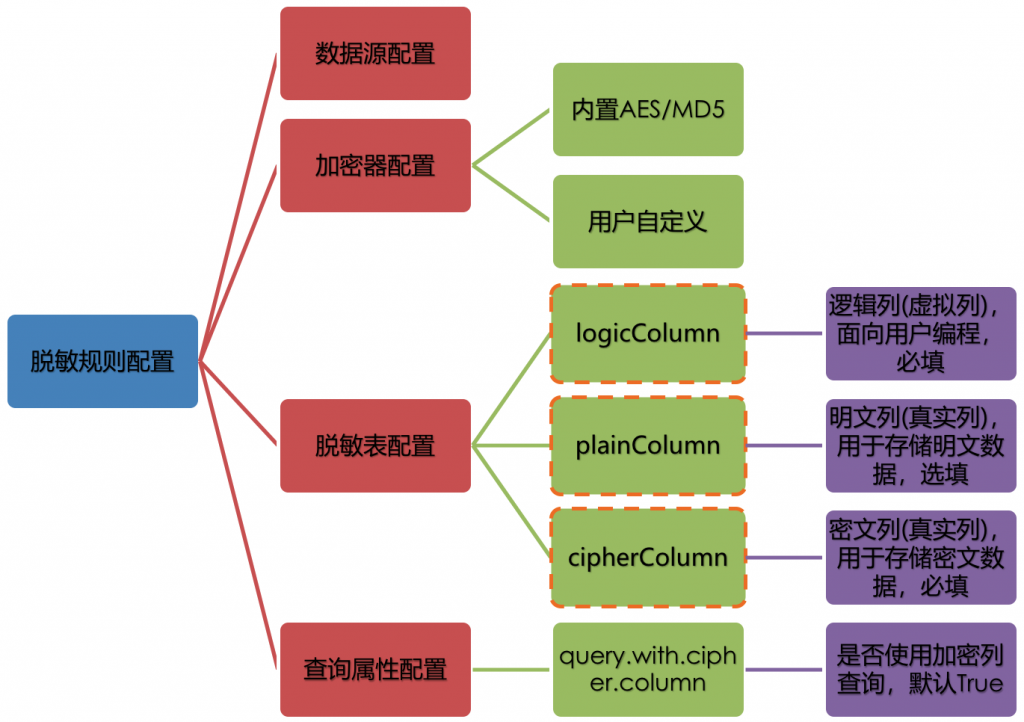
脱敏配置主要分为四部分:数据源配置,加密器配置,脱敏表配置以及查询属性配置,其详情如下图所示:
- 数据源配置:指DataSource的配置信息
- 加密器配置:指使用什么加密策略进行加解密。目前ShardingSphere内置了两种加解密策略:AES/MD5
- 脱敏表配置:指定哪个列用于存储密文数据(cipherColumn)、哪个列用于存储明文数据(plainColumn)以及用户想使用哪个列进行SQL编写(logicColumn)
- 查询属性的配置:当底层数据库表里同时存储了明文数据、密文数据后,该属性开关用于决定是直接查询数据库表里的明文数据进行返回,还是查询密文数据通过Encrypt-JDBC解密后返回
脱敏处理流程
下图可以看出ShardingSphere将逻辑列与明文列和密文列进行了列名映射。
下方图片展示了使用Encrypt-JDBC进行增删改查时,其中的处理流程和转换逻辑,如下图所示。
加密策略解析
ShardingSphere提供了两种加密策略用于数据脱敏,该两种策略分别对应ShardingSphere的两种加解密的接口,即Encryptor和QueryAssistedEncryptor。
Encryptor:该解决方案通过提供encrypt(),decrypt()两种方法对需要脱敏的数据进行加解密。在用户进行INSERT,DELETE,UPDATE时,ShardingSphere会按照用户配置,对SQL进行解析、改写、路由,并会调用encrypt()将数据加密后存储到数据库, 而在SELECT时,则调用decrypt()方法将从数据库中取出的脱敏数据进行逆向解密,最终将原始数据返回给用户。当前,ShardingSphere针对这种类型的脱敏解决方案提供了两种具体实现类,分别是MD5(不可逆),AES(可逆),用户只需配置即可使用这两种内置的方案QueryAssistedEncryptor:相比较于第一种脱敏方案,该方案更为安全和复杂。它的理念是:即使是相同的数据,如两个用户的密码相同,它们在数据库里存储的脱敏数据也应当是不一样的。这种理念更有利于保护用户信息,防止撞库成功。它提供三种函数进行实现,分别是encrypt(), decrypt(), queryAssistedEncrypt()。在encrypt()阶段,用户通过设置某个变动种子,例如时间戳。针对原始数据+变动种子组合的内容进行加密,就能保证即使原始数据相同,也因为有变动种子的存在,致使加密后的脱敏数据是不一样的。在decrypt()可依据之前规定的加密算法,利用种子数据进行解密。queryAssistedEncrypt()用于生成辅助查询列,用于原始数据的查询过程。当前,ShardingSphere针对这种类型的脱敏解决方案并没有提供具体实现类,却将该理念抽象成接口,提供给用户自行实现。ShardingSphere将调用用户提供的该方案的具体实现类进行数据脱敏
数据脱敏实战
我们的实战基于博文MySQL之Sharding-JDBC数据分片中的实战案例。
我们在sharding-jdbc-demo项目中新建配置文件application-encryptor.properties:
# datasource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names=ds0
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds0.type=com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds0.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds0.jdbc-url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/rubin_shard_1?characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useSSL=false&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds0.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds0.password=123456
# encrypt
spring.shardingsphere.encrypt.tables.c_user.columns.pwd.plain-column=pwd_plain
spring.shardingsphere.encrypt.tables.c_user.columns.pwd.cipher-column=pwd_cipher
spring.shardingsphere.encrypt.encryptors.rubin_pwd.type=aes
spring.shardingsphere.encrypt.encryptors.rubin_pwd.props.aes.key.value=rubin
spring.shardingsphere.encrypt.tables.c_user.columns.pwd.encryptor=rubin_pwd
# true 加密逻辑列之后查询加密列 并解密返回 false 直接查询明文列并返回
spring.shardingsphere.props.query.with.cipher.column=false
修改配置文件application.properties中的profile:
#spring.profiles.active=sharding-database
#spring.profiles.active=master-slave
#spring.profiles.active=hint-database
spring.profiles.active=encryptor
spring.shardingsphere.props.sql.show=true创建测试类:
package com.rubin.shardingjdbcdemo;
import com.rubin.shardingjdbcdemo.entity.CUser;
import com.rubin.shardingjdbcdemo.repository.CUserRepository;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.annotation.Repeat;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import java.util.List;
@SpringBootTest(classes = ShardingJdbcDemoApplication.class)
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
public class TestEncryptor {
@Autowired
private CUserRepository userRepository;
@Test
@Repeat(2)
public void testAdd() {
CUser user = new CUser();
user.setName("tiger");
user.setPwd("abc");
userRepository.save(user);
}
@Test
public void testFind() {
List<CUser> list = userRepository.findByPwd("abc");
list.forEach(cUser -> {
System.out.println(cUser.getId() + " " + cUser.getName() + " " + cUser.getPwd());
});
}
}
运行上述测试类,我们会发现我们的插入操作在存库时会自动加密成密文,查询时会自动解密。
本博文内容到此就结束了,欢迎小伙伴们积极留言交流~~~


文章评论