高级映射
地理坐标点数据类型
地理坐标点
地理坐标点是指地球表面可以用经纬度描述的一个点。 地理坐标点可以用来计算两个坐标间的距离,还可以判断一个坐标是否在一个区域中。地理坐标点需要显式声明对应字段类型为geo_point:
示例:
PUT /company-locations
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "text"
},
"location": {
"type": "geo_point"
}
}
}
}经纬度坐标格式
如上例,location字段被声明为geo_point后,我们就可以索引包含了经纬度信息的文档了。 经纬度信息的形式可以是字符串、数组或者对象
# 字符串形式
PUT /company-locations/_doc/1
{
"name": "NetEase",
"location": "40.715,74.011"
}
# 对象形式
PUT /company-locations/_doc/2
{
"name": "Sina",
"location": {
"lat": 40.722,
"lon": 73.989
}
}
# 数组形式
PUT /company-locations/_doc/3
{
"name": "Baidu",
"location": [
73.983,
40.719
]
}注意:
- 字符串形式以半角逗号分割,如 "lat,lon"
- 对象形式显式命名为lat和lon
- 数组形式表示为 [lon,lat]
通过地理坐标点过滤
有四种地理坐标点相关的过滤器 可以用来选中或者排除文档:
| 过滤器 | 作用 |
| geo_bounding_box | 找出落在指定矩形框中的点 |
| geo_distance | 找出与指定位置在给定距离内的点 |
| geo_distance_range | 找出与指定点距离在给定最小距离和最大距离之间的点 |
| geo_polygon | 找出落在多边形中的点。 这个过滤器使用代价很大 。当你觉得自己需要使用它,最好先看看 geo-shapes |
geo_bounding_box查询
这是目前为止最有效的地理坐标过滤器了,因为它计算起来非常简单。 你指定一个矩形的顶部,底部 ,左边界和右边界,然后过滤器只需判断坐标的经度是否在左右边界之间,纬度是否在上下边界之间。
查询示例:
GET /company-locations/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": {
"match_all": {}
},
"filter": {
"geo_bounding_box": {
"location": {
"top_left": {
"lat": 40.73,
"lon": 71.12
},
"bottom_right": {
"lat": 40.01,
"lon": 74.1
}
}
}
}
}
}
}geo_distance
过滤仅包含与地理位置相距特定距离内的匹配的文档。假设以下映射和索引文档,然后可以使用geo_distance过滤器执行以下查询。
查询示例:
GET /company-locations/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": {
"match_all": {}
},
"filter": {
"geo_distance": {
"distance": "1km",
"location": {
"lat": 40.715,
"lon": 74.011
}
}
}
}
}
}动态映射
Elasticsearch在遇到文档中以前未遇到的字段,可以使用dynamic mapping(动态映射机制)来确定字段的数据类型并自动把新的字段添加到类型映射。
Elasticsearch的动态映射机制可以进行开关控制,通过设置mappings的dynamic属性,dynamic有如下设置项:
- true:遇到陌生字段就执行
dynamic mapping处理机制 - false:遇到陌生字段就忽略
- strict:遇到陌生字段就报错
使用示例:
# 设置为报错
PUT /user
{
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": 3,
"number_of_replicas": 0
},
"mappings": {
"dynamic": "strict",
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "text"
},
"address": {
"type": "object",
"dynamic": true
}
}
}
}
# 插入以下文档,将会报错
# user索引层设置dynamic是strict,在user层内设置age将报错
# 在address层设置dynamic是ture,将动态映射生成字段
PUT /user/_doc/1
{
"name": "lisi",
"age": "20",
"address": {
"province": "beijing",
"city": "beijing"
}
}
PUT /user
{
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": 3,
"number_of_replicas": 0
},
"mappings": {
"dynamic": true,
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "text"
},
"address": {
"type": "object",
"dynamic": true
}
}
}
}自定义动态映射
如果你想在运行时增加新的字段,你可能会启用动态映射。 然而,有时候,动态映射规则可能不太智能。幸运的是,我们可以通过设置去自定义这些规则,以便更好的适用于你的数据。
日期检测
当Elasticsearch遇到一个新的字符串字段时,它会检测这个字段是否包含一个可识别的日期,比如2014-01-01。如果它像日期,这个字段就会被作为date类型添加。否则,它会被作为string类型添加。有些时候这个行为可能导致一些问题。想象下,你有如下这样的一个文档:{ "note": "2014-01-01" },假设这是第一次识别note字段,它会被添加为date字段。但是如果下一个文档像这样:{ "note": "Logged out" },这显然不是一个日期,但为时已晚。这个字段已经是一个日期类型,这个不合法的日期将会造成一个异常。
日期检测可以通过在根对象上设置date_detection为false来关闭。
示例:
PUT /my_index
{
"mappings": {
"date_detection": false
}
}使用这个映射,字符串将始终作为string类型。如果需要一个date字段,必须手动添加。Elasticsearch判断字符串为日期的规则可以通过dynamic_date_formats setting来设置。
示例:
PUT /my_index
{
"mappings": {
"dynamic_date_formats": "MM/dd/yyyy"
}
}dynamic_templates
使用dynamic_templates可以完全控制新生成字段的映射,甚至可以通过字段名称或数据类型来应用不同的映射。每个模板都有一个名称,你可以用来描述这个模板的用途,一个mapping来指定映射应该怎样使用,以及至少一个参数 (如 match) 来定义这个模板适用于哪个字段。
模板按照顺序来检测,第一个匹配的模板会被启用。例如,我们给string类型字段定义两个模板:
- es :以_es结尾的字段名需要使用
spanish分词器 - en :所有其他字段使用
english分词器
我们将es模板放在第一位,因为它比匹配所有字符串字段的en模板更特殊:
PUT /my_index2
{
"mappings": {
"dynamic_templates": [
{
"es": {
"match": "*_es",
"match_mapping_type": "string",
"mapping": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "spanish"
}
}
},
{
"en": {
"match": "*",
"match_mapping_type": "string",
"mapping": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "english"
}
}
}
]
}
}match参数只匹配字段名称,path_match参数匹配字段在对象上的完整路径,所以 address.*.name将匹配这样的字段:
{
"address": {
"city": {
"name": "New York"
}
}
}Query DSL
文档地址:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.3/query-dsl.html。
Elasticsearch提供了基于JSON的完整查询DSL(Domain Specific Language 特定域的语言)来定义查询。将查询DSL视为查询的AST(抽象语法树),它由两种子句组成:
- 叶子查询子句:叶子查询子句在特定域中寻找特定的值,如
match,term或range查询 - 复合查询子句:复合查询子句包装其他叶子查询或复合查询,并用于以逻辑方式组合多个查询(例如
bool或dis_max查询),或更改其行为(例如constant_score查询)
我们在使用ElasticSearch的时候,避免不了使用DSL语句去查询,就像使用关系型数据库的时候要学会SQL语法一样。如果我们学习好了DSL语法的使用,那么在日后使用和使用Java Client调用时候也会变得非常简单。
基本语法:
POST /索引库名/_search
{
"query":{
"查询类型":{
"查询条件":"查询条件值"
}
}
}这里的query代表一个查询对象,里面可以有不同的查询属性:
- 查询类型:例如:
match_all,match,term,range等等 - 查询条件:查询条件会根据类型的不同,写法也有差异
查询所有(match_all query)
示例:
POST /rubin_user_index/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}- query:代表查询对象
- match_all:代表查询所有
结果字段:
{
# 查询花费时间,单位是毫秒
"took" : 0,
# 是否超时
"timed_out" : false,
# 分片信息
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
# 搜索结果总览对象
"hits" : {
# 搜索到的总条数
"total" : {
"value" : 1,
"relation" : "eq"
},
# 所有结果中文档得分的最高分
"max_score" : 1.0,
# 搜索结果的文档对象数组,每个元素是一条搜索到的文档信息
"hits" : [
{
# 索引库
"_index" : "rubin_user_index",
# 文档类型
"_type" : "_doc",
# 文档id
"_id" : "1",
# 文档得分
"_score" : 1.0,
# 文档的源数据
"_source" : {
"name" : "rubin",
"motto" : "人生不止眼前的苟且",
"nickname" : "虾米",
"age" : 27
}
}
]
}
}全文搜索(full-text query)
全文搜索能够搜索已分析的文本字段,如电子邮件正文,商品描述等。使用索引期间应用于字段的同一分析器处理查询字符串。全文搜索的分类很多几个典型的如下:
匹配搜索(match query)
全文查询的标准查询,它可以对一个字段进行模糊、短语查询。match queries接收text/numerics/dates,对它们进行分词分析,再组织成一个boolean查询。可通过operator指定bool组合操作(or、and默认是or)。
现在,索引库中有2部手机,1台电视:
PUT /rubin_property
{
"settings": {},
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"title": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word"
},
"images": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"price": {
"type": "float"
}
}
}
}
POST /rubin_property/_doc/
{
"title": "小米电视4A",
"images": "http://image.rubin.com/12479122.jpg",
"price": 4288
}
POST /rubin_property/_doc/
{
"title": "小米手机",
"images": "http://image.rubin.com/12479622.jpg",
"price": 2699
}
POST /rubin_property/_doc/
{
"title": "华为手机",
"images": "http://image.rubin.com/12479922.jpg",
"price": 5699
}or关系
match类型查询,会把查询条件进行分词,然后进行查询,多个词条之间是or的关系:
POST /rubin_property/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"title": "小米电视4A"
}
}
}结果:
{
"took" : 264,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 2,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 2.8330114,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "rubin_property",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "iNYDf30B1ct5FZWHyJ7B",
"_score" : 2.8330114,
"_source" : {
"title" : "小米电视4A",
"images" : "http://image.rubin.com/12479122.jpg",
"price" : 4288
}
},
{
"_index" : "rubin_property",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "idYDf30B1ct5FZWH1J6M",
"_score" : 0.52354836,
"_source" : {
"title" : "小米手机",
"images" : "http://image.rubin.com/12479622.jpg",
"price" : 2699
}
}
]
}
}
在上面的案例中,不仅会查询到电视,而且与小米相关的都会查询到,多个词之间是or的关系。
and关系
某些情况下,我们需要更精确查找,我们希望这个关系变成and,可以这样做:
POST /rubin_property/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"title": {
"query": "小米电视4A",
"operator": "and"
}
}
}
}结果:
{
"took" : 4,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 1,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 2.8330114,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "rubin_property",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "iNYDf30B1ct5FZWHyJ7B",
"_score" : 2.8330114,
"_source" : {
"title" : "小米电视4A",
"images" : "http://image.rubin.com/12479122.jpg",
"price" : 4288
}
}
]
}
}本例中,只有同时包含小米和电视的词条才会被搜索到。
match模式会对搜索keyword先分词,再匹配。
短语搜索(match phrase query)
match_phrase查询用来对一个字段进行短语查询,可以指定analyzer、slop移动因子:
GET /rubin_property/_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase": {
"title": "小米电视"
}
}
}
GET /rubin_property/_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase": {
"title": "小米 4A"
}
}
}
GET /rubin_property/_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase": {
"title": {
"query": "小米 4A",
"slop": 2
}
}
}
}短语搜索不会对搜索keyword进行分词,而是直接匹配文档字段分词后的词条。
query_string查询
Query String Query提供了无需指定某字段而对文档全文进行匹配查询的一个高级查询,同时可以指定在哪些字段上进行匹配。
# 默认 和 指定字段
GET /rubin_property/_search
{
"query": {
"query_string": {
"query": "2699"
}
}
}
GET /rubin_property/_search
{
"query": {
"query_string": {
"query": "2699",
"default_field": "title"
}
}
}
# 逻辑查询
GET /rubin_property/_search
{
"query": {
"query_string": {
"query": "手机 OR 小米",
"default_field": "title"
}
}
}
GET /rubin_property/_search
{
"query": {
"query_string": {
"query": "手机 AND 小米",
"default_field": "title"
}
}
}
# 模糊查询
GET /rubin_property/_search
{
"query": {
"query_string": {
"query": "大米~1",
"default_field": "title"
}
}
}
# 多字段支持
GET /rubin_property/_search
{
"query": {
"query_string": {
"query": "2699",
"fields": [
"title",
"price"
]
}
}
}多字段匹配搜索(multi match query)
如果你需要在多个字段上进行文本搜索,可用multi_match 。multi_match在match的基础上支持对多个字段进行文本查询。
GET /rubin_property/_search
{
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": "2699",
"fields": [
"title",
"price"
]
}
}
}还可以使用*匹配多个字段:
GET /rubin_property/_search
{
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": "http://image.rubin.com/12479622.jpg",
"fields": [
"title",
"ima*"
]
}
}
}词条级搜索(term-level queries)
可以使用term-level queries根据结构化数据中的精确值查找文档。结构化数据的值包括日期范围、IP地址、价格或产品ID。
与全文查询不同,term-level queries不分析搜索词。相反,词条与存储在字段级别中的术语完全匹配。
PUT /book
{
"settings": {},
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"description": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word"
},
"name": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word"
},
"price": {
"type": "float"
},
"timestamp": {
"type": "date",
"format": "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss||yyyy-MM-dd||epoch_millis"
}
}
}
}
PUT /book/_doc/1
{
"name": "lucene",
"description": "Lucene Core is a Java library providing powerful indexing and search features, as well as spellchecking,hit highlighting and advanced analysis/tokenization capabilities. The PyLucene sub project provides Python bindings for Lucene Core. ",
"price": 100.45,
"timestamp": "2020-08-21 19:11:35"
}
PUT /book/_doc/2
{
"name": "solr",
"description": "Solr is highly scalable, providing fully fault tolerant distributed indexing, search and analytics. It exposes Lucenes features through easy to use JSON/HTTP interfaces or native clients for Java and other languages.",
"price": 320.45,
"timestamp": "2020-07-21 17:11:35"
}
PUT /book/_doc/3
{
"name": "Hadoop",
"description": "The Apache Hadoop software library is a framework that allows for the distributed processing of large data sets across clusters of computers using simple programming models.",
"price": 620.45,
"timestamp": "2020-08-22 19:18:35"
}
PUT /book/_doc/4
{
"name": "ElasticSearch",
"description": "Elasticsearch是一个基于Lucene的搜索服务器。它提供了一个分布式多用户能力 的全文搜索引擎,基于RESTful web接口。Elasticsearch是用Java语言开发的,并作为Apache许可条 款下的开放源码发布,是一种流行的企业级搜索引擎。Elasticsearch用于云计算中,能够达到实时搜 索,稳定,可靠,快速,安装使用方便。官方客户端在Java、.NET(C#)、PHP、Python、Apache Groovy、Ruby和许多其他语言中都是可用的。根据DB-Engines的排名显示,Elasticsearch是最受欢 迎的企业搜索引擎,其次是Apache Solr,也是基于Lucene。",
"price": 999.99,
"timestamp": "2020-08-15 10:11:35"
}词条搜索(term query)
term查询用于查询指定字段包含某个词项的文档:
POST /book/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"name": "solr"
}
}
}词条集合搜索(terms query)
terms查询用于查询指定字段包含某些词项的文档:
GET /book/_search
{
"query": {
"terms": {
"name": [
"solr",
"elasticsearch"
]
}
}
}范围搜索(range query)
- gte:大于等于
- gt:大于
- lte:小于等于
- lt:小于
- boost:查询权重
GET /book/_search
{
"query": {
"range": {
"price": {
"gte": 10,
"lte": 200,
"boost": 2
}
}
}
}
GET /book/_search
{
"query": {
"range": {
"timestamp": {
"gte": "now-2d/d",
"lt": "now/d"
}
}
}
}
GET book/_search
{
"query": {
"range": {
"timestamp": {
"gte": "18/08/2020",
"lte": "2021",
"format": "dd/MM/yyyy||yyyy"
}
}
}
}不为空搜索(exists query)
查询指定字段值不为空的文档。相当SQL中的column is not null。
GET /book/_search
{
"query": {
"exists": {
"field": "price"
}
}
}词项前缀搜索(prefix query)
GET /book/_search
{
"query": {
"prefix": {
"name": "so"
}
}
}通配符搜索(wildcard query)
GET /book/_search
{
"query": {
"wildcard": {
"name": "so*r"
}
}
}
GET /book/_search
{
"query": {
"wildcard": {
"name": {
"value": "lu*",
"boost": 2
}
}
}
}正则搜索(regexp query)
regexp允许使用正则表达式进行term查询。注意regexp如果使用不正确,会给服务器带来很严重的性能压力。比如.*开头的查询,将会匹配所有的倒排索引中的关键字,这几乎相当于全表扫描,会很慢。因此如果可以的话,最好在使用正则前,加上匹配的前缀。
GET /book/_search
{
"query": {
"regexp": {
"name": "s.*"
}
}
}
GET /book/_search
{
"query": {
"regexp": {
"name": {
"value": "s.*",
"boost": 1.2
}
}
}
}模糊搜索(fuzzy query)
GET /book/_search
{
"query": {
"fuzzy": {
"name": "so"
}
}
}
GET /book/_search
{
"query": {
"fuzzy": {
"name": {
"value": "so",
"boost": 1,
"fuzziness": 2
}
}
}
}
GET /book/_search
{
"query": {
"fuzzy": {
"name": {
"value": "sorl",
"boost": 1,
"fuzziness": 2
}
}
}
}ids搜索(id集合查询)
GET /book/_search
{
"query": {
"ids": {
"values": [
"1",
"3"
]
}
}
}复合搜索(compound query)
constant_score query
用来包装另一个查询,将查询匹配的文档的评分设为一个常值:
GET /book/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"description": "solr"
}
}
}
GET /book/_search
{
"query": {
"constant_score": {
"filter": {
"term": {
"description": "solr"
}
},
"boost": 1.2
}
}
}布尔搜索(bool query)
bool查询用bool操作来组合多个查询字句为一个查询。 可用的关键字:
- must:必须满足
- filter:必须满足,但执行的是filter上下文,不参与、不影响评分
- should:或
- must_not:必须不满足
POST /book/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": {
"match": {
"description": "java"
}
},
"filter": {
"term": {
"name": "solr"
}
},
"must_not": {
"range": {
"price": {
"gte": 200,
"lte": 300
}
}
},
"minimum_should_match": 1,
"boost": 1
}
}
}minimum_should_match代表了最小匹配精度,如果设置minimum_should_match=1,那么should语句中至少需要有一个条件满足。
排序
相关性评分排序
默认情况下,返回的结果是按照相关性进行排序的——最相关的文档排在最前。 在本章的后面部分,我们会解释相关性意味着什么以及它是如何计算的, 不过让我们首先看看sort参数以及如何使用它。
为了按照相关性来排序,需要将相关性表示为一个数值。在 Elasticsearch 中, 相关性得分由一个浮点数进行表示,并在搜索结果中通过_score参数返回, 默认排序是_score降序,按照相关性评分升序排序如下:
POST /book/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"description": "solr"
}
}
}
POST /book/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"description": "solr"
}
},
"sort": [
{
"_score": {
"order": "asc"
}
}
]
}字段值排序
POST /book/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"sort": [
{
"price": {
"order": "desc"
}
}
]
}多级排序
假定我们想要结合使用price和_score(得分)进行查询,并且匹配的结果首先按照价格排序,然后按照相关性得分排序:
POST /book/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"sort": [
{
"price": {
"order": "desc"
}
},
{
"timestamp": {
"order": "desc"
}
}
]
}分页
Elasticsearch中实现分页的语法非常简单:
POST /book/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"size": 2,
"from": 0
}
POST /book/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"sort": [
{
"price": {
"order": "desc"
}
}
],
"size": 2,
"from": 2
}- size:每页显示多少条
- from:当前页起始索引,
int start = (pageNum - 1) * size
高亮
Elasticsearch中实现高亮的语法比较简单:
POST /book/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"name": "elasticsearch"
}
},
"highlight": {
"pre_tags": "<font color='pink'>",
"post_tags": "</font>",
"fields": [
{
"name": {}
}
]
}
}
POST /book/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"name": "elasticsearch"
}
},
"highlight": {
"pre_tags": "<font color='pink'>",
"post_tags": "</font>",
"fields": [
{
"name": {}
},
{
"description": {}
}
]
}
}
POST /book/_search
{
"query": {
"query_string": {
"query": "elasticsearch"
}
},
"highlight": {
"pre_tags": "<font color='pink'>",
"post_tags": "</font>",
"fields": [
{
"name": {}
},
{
"description": {}
}
]
}
}在使用match查询的同时,加上一个highlight属性:
- pre_tags:前置标签
- post_tags:后置标签
- fields:需要高亮的字段
fields中:
- name:这里声明
title字段需要高亮,后面可以为这个字段设置特有配置,也可以空
结果:
{
"took" : 3,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 1,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 1.6317781,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "book",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "4",
"_score" : 1.6317781,
"_source" : {
"name" : "ElasticSearch",
"description" : "Elasticsearch是一个基于Lucene的搜索服务器。它提供了一个分布式多用户能力 的全文搜索引擎,基于RESTful web接口。Elasticsearch是用Java语言开发的,并作为Apache许可条 款下的开放源码发布,是一种流行的企业级搜索引擎。Elasticsearch用于云计算中,能够达到实时搜 索,稳定,可靠,快速,安装使用方便。官方客户端在Java、.NET(C#)、PHP、Python、Apache Groovy、Ruby和许多其他语言中都是可用的。根据DB-Engines的排名显示,Elasticsearch是最受欢 迎的企业搜索引擎,其次是Apache Solr,也是基于Lucene。",
"price" : 999.99,
"timestamp" : "2020-08-15 10:11:35"
},
"highlight" : {
"name" : [
"<font color='pink'>ElasticSearch</font>"
],
"description" : [
"<font color='pink'>Elasticsearch</font>是一个基于Lucene的搜索服务器。它提供了一个分布式多用户能力 的全文搜索引擎,基于RESTful web接口。",
"<font color='pink'>Elasticsearch</font>是用Java语言开发的,并作为Apache许可条 款下的开放源码发布,是一种流行的企业级搜索引擎。",
"<font color='pink'>Elasticsearch</font>用于云计算中,能够达到实时搜 索,稳定,可靠,快速,安装使用方便。",
"根据DB-Engines的排名显示,<font color='pink'>Elasticsearch</font>是最受欢 迎的企业搜索引擎,其次是Apache Solr,也是基于Lucene。"
]
}
}
]
}
}
文档批量操作(bulk和mget)
mget 批量查询
单条查询 GET /test_index/_doc/1,如果查询多个id的文档一条一条查询,网络开销太大。
GET /_mget
{
"docs": [
{
"_index": "book",
"_id": 1
},
{
"_index": "book",
"_id": 2
}
]
}返回:
{
"docs" : [
{
"_index" : "book",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_version" : 1,
"_seq_no" : 0,
"_primary_term" : 1,
"found" : true,
"_source" : {
"name" : "lucene",
"description" : "Lucene Core is a Java library providing powerful indexing and search features, as well as spellchecking,hit highlighting and advanced analysis/tokenization capabilities. The PyLucene sub project provides Python bindings for Lucene Core. ",
"price" : 100.45,
"timestamp" : "2020-08-21 19:11:35"
}
},
{
"_index" : "book",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "2",
"_version" : 1,
"_seq_no" : 1,
"_primary_term" : 1,
"found" : true,
"_source" : {
"name" : "solr",
"description" : "Solr is highly scalable, providing fully fault tolerant distributed indexing, search and analytics. It exposes Lucenes features through easy to use JSON/HTTP interfaces or native clients for Java and other languages.",
"price" : 320.45,
"timestamp" : "2020-07-21 17:11:35"
}
}
]
}同一索引下批量查询:
GET /book/_mget
{
"docs": [
{
"_id": 2
},
{
"_id": 3
}
]
}搜索简化写法:
POST /book/_search
{
"query": {
"ids": {
"values": [
"1",
"4"
]
}
}
}bulk 批量增删改
Bulk操作解释将文档的增删改查一些列操作,通过一次请求全都做完。减少网络传输次数。
语法:
POST /_bulk
{"action": {"metadata"}}
{"data"}如下操作,删除1,新增5,修改2。
POST /_bulk
{"delete":{"_index":"book","_id":"1"}}
{"create":{"_index":"book","_id":"5"}}
{"name":"test14","price":100.99}
{"update":{"_index":"book","_id":"2"}}
{"doc":{"name":"test"}}功能:
- delete:删除一个文档,只要1个json串就可以了,删除的批量操作不需要请求体
- create:相当于强制创建---
PUT /index/type/id/_create - index:普通的
PUT操作,可以是创建文档,也可以是全量替换文档 - update:执行的是局部更新
partial update操作
格式:每个json不能换行,相邻json必须换行。
隔离:每个操作互不影响,操作失败的行会返回其失败信息。
实际用法:bulk请求一次不要太大,否则一下积压到内存中,性能会下降。所以,一次请求几千个操作、大小在几M正好。
bulk会将要处理的数据载入内存中,所以数据量是有限的,最佳的数据两不是一个确定的数据,它取决于你的硬件,你的文档大小以及复杂性,你的索引以及搜索的负载。
一般建议是1000-5000个文档,大小建议是5-15MB,默认不能超过100M,可以在es的配置文件(ES的config下的elasticsearch.yml)中配置。
http.max_content_length: 10mbFilter DSL
Elasticsearch中的所有的查询都会触发相关度得分的计算。对于那些我们不需要相关度得分的场景下,Elasticsearch以过滤器的形式提供了另一种查询功能,过滤器在概念上类似于查询,但是它们有非常快的执行速度,执行速度快主要有以下两个原因:
- 过滤器不会计算相关度的得分,所以它们在计算上更快一些
- 过滤器可以被缓存到内存中,这使得在重复的搜索查询上,其要比相应的查询快出许多
为了理解过滤器,可以将一个查询(像是match_all,match,bool等)和一个过滤器结合起来。我们以范围过滤器为例,它允许我们通过一个区间的值来过滤文档。这通常被用在数字和日期的过滤上。下面这个例子使用一个被过滤的查询,其返回price值是在200到1000之间(闭区间)的书。
示例:
POST /book/_search
{
"query": {
"filtered": {
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"filter": {
"range": {
"price": {
"gte": 200,
"lte": 1000
}
}
}
}
}
}
#5.0 之后的写法
POST /book/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": {
"match_all": {}
},
"filter": {
"range": {
"price": {
"gte": 200,
"lte": 1000
}
}
}
}
}
}分解上面的例子,被过滤的查询包含一个match_all查询(查询部分)和一个过滤器(filter部分)。我们可以在查询部分中放入其他查询,在filter部分放入其它过滤器。在上面的应用场景中,由于所有的在这个范围之内的文档都是平等的(或者说相关度都是一样的),没有一个文档比另一个文档更相关,所以这个时候使用范围过滤器就非常合适了。通常情况下,要决定是使用过滤器还是使用查询,你就需要问自己是否需要相关度得分。如果相关度是不重要的,使用过滤器,否则使用查询。查询和过滤器在概念上类似于SELECT WHERE语句。
定位非法搜索及原因
在开发的时候,我们可能会写到上百行的查询语句,如果出错的话,找起来很麻烦,Elasticsearch提供了帮助开发人员定位不合法的查询的api:_validate。
示例:
GET /book/_search?explain
{
"query": {
"match1": {
"name": "test"
}
}
}
# 使用 validate
GET /book/_validate/query?explain
{
"query": {
"match1": {
"name": "test"
}
}
}返回结果:
{
"valid" : false,
"error" : "org.elasticsearch.common.ParsingException: no [query] registered for [match1]"
}正确查询返回:
{
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"failed" : 0
},
"valid" : true,
"explanations" : [
{
"index" : "book",
"valid" : true,
"explanation" : "name:test"
}
]
}聚合分析
聚合介绍
聚合分析是数据库中重要的功能特性,完成对一个查询的数据集中数据的聚合计算,如:找出某字段(或计算表达式的结果)的最大值、最小值,计算和、平均值等。Elasticsearch作为搜索引擎兼数据库,同样提供了强大的聚合分析能力。
对一个数据集求最大、最小、和、平均值等指标的聚合,在ES中称为指标聚合metric而关系型数据库中除了有聚合函数外,还可以对查询出的数据进行分组group by,再在组上进行指标聚合。在ES中group by称为分桶,桶聚合bucketing。
Elasticsearch聚合分析语法:
"aggregations" : {
"<aggregation_name>" : { <!--聚合的名字 -->
"<aggregation_type>" : { <!--聚合的类型 -->
<aggregation_body> <!--聚合体:对哪些字段进行聚合 -->
}
[,"meta" : { [<meta_data_body>] } ]? <!--元 -->
[,"aggregations" : { [<sub_aggregation>]+ } ]? <!--在聚合里面在定义子聚合 -
->
}
[,"<aggregation_name_2>" : { ... } ]*<!--聚合的名字 -->
}说明:aggregations也可简写为aggs。
指标聚合
max min sum avg
示例:查询所有书中最贵的:
POST /book/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"max_price": {
"max": {
"field": "price"
}
}
}
}文档计数count
示例:统计price大于100的文档数量:
POST /book/_count
{
"query": {
"range": {
"price": {
"gt": 100
}
}
}
}value_count 统计某字段有值的文档数
POST /book/_search?size=0
{
"aggs": {
"price_count": {
"value_count": {
"field": "price"
}
}
}
}cardinality值去重计数、基数
POST /book/_search?size=0
{
"aggs": {
"_id_count": {
"cardinality": {
"field": "_id"
}
},
"price_count": {
"cardinality": {
"field": "price"
}
}
}
}stats 统计 count max min avg sum5 个值
POST /book/_search?size=0
{
"aggs": {
"price_stats": {
"stats": {
"field": "price"
}
}
}
}Extended stats
高级统计,比stats多4个统计结果: 平方和、方差、标准差、平均值加/减两个标准差的区间:
POST /book/_search?size=0
{
"aggs": {
"price_stats": {
"extended_stats": {
"field": "price"
}
}
}
}Percentiles 占比百分位对应的值统计
POST /book/_search?size=0
{
"aggs": {
"price_percents": {
"percentiles": {
"field": "price"
}
}
}
}指定分位值:
POST /book/_search?size=0
{
"aggs": {
"price_percents": {
"percentiles": {
"field": "price",
"percents" : [75, 99, 99.9]
}
}
}
}Percentiles rank 统计值小于等于指定值的文档占比
统计price小于100和200的文档的占比:
POST /book/_search?size=0
{
"aggs": {
"gge_perc_rank": {
"percentile_ranks": {
"field": "price",
"values": [
100,
200
]
}
}
}
}桶聚合
官方文档地址:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.3/search-aggregations-bucket.html。
它执行的是对文档分组的操作(与sql中的group by类似),把满足相关特性的文档分到一个桶里,输出结果往往是一个个包含多个文档的桶(一个桶就是一个group)。
- bucket:一个数据分组
- metric:对一个数据分组执行的统计
POST /book/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"group_by_price": {
"range": {
"field": "price",
"ranges": [
{
"from": 0,
"to": 200
},
{
"from": 200,
"to": 400
},
{
"from": 400,
"to": 1000
}
]
},
"aggs": {
"average_price": {
"avg": {
"field": "price"
}
}
}
}
}
}值的个数统计结果:
{
"took" : 3,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 4,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : null,
"hits" : [ ]
},
"aggregations" : {
"group_by_price" : {
"buckets" : [
{
"key" : "0.0-200.0",
"from" : 0.0,
"to" : 200.0,
"doc_count" : 1,
"average_price" : {
"value" : 100.98999786376953
}
},
{
"key" : "200.0-400.0",
"from" : 200.0,
"to" : 400.0,
"doc_count" : 1,
"average_price" : {
"value" : 320.45001220703125
}
},
{
"key" : "400.0-1000.0",
"from" : 400.0,
"to" : 1000.0,
"doc_count" : 2,
"average_price" : {
"value" : 810.2200012207031
}
}
]
}
}
}实现having效果:
POST /book/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"group_by_price": {
"range": {
"field": "price",
"ranges": [
{
"from": 0,
"to": 200
},
{
"from": 200,
"to": 400
},
{
"from": 400,
"to": 1000
}
]
},
"aggs": {
"average_price": {
"avg": {
"field": "price"
}
},
"having": {
"bucket_selector": {
"buckets_path": {
"avg_price": "average_price"
},
"script": {
"source": "params.avg_price >= 200"
}
}
}
}
}
}
}零停机索引重建
说明
Elasticsearch是一个实时的分布式搜索引擎,为用户提供搜索服务,当我们决定存储某种数据时,在创建索引的时候需要数据结构完整确定下来,与此同时索引的设定和很多固定配置将不能改变。当需要改变数据结构时就需要重建索引。为此,Elasticsearch团队提供了辅助工具帮助开发人员进行索引重建。
方案一 外部数据导入方案
整体介绍
系统架构设计中,有关系型数据库用来存储数据,Elasticsearch在系统架构里起到查询加速的作用,如果遇到索引重建的操作,待系统模块发布新版本后,可以从数据库将数据查询出来,重新灌到Elasticsearch即可。
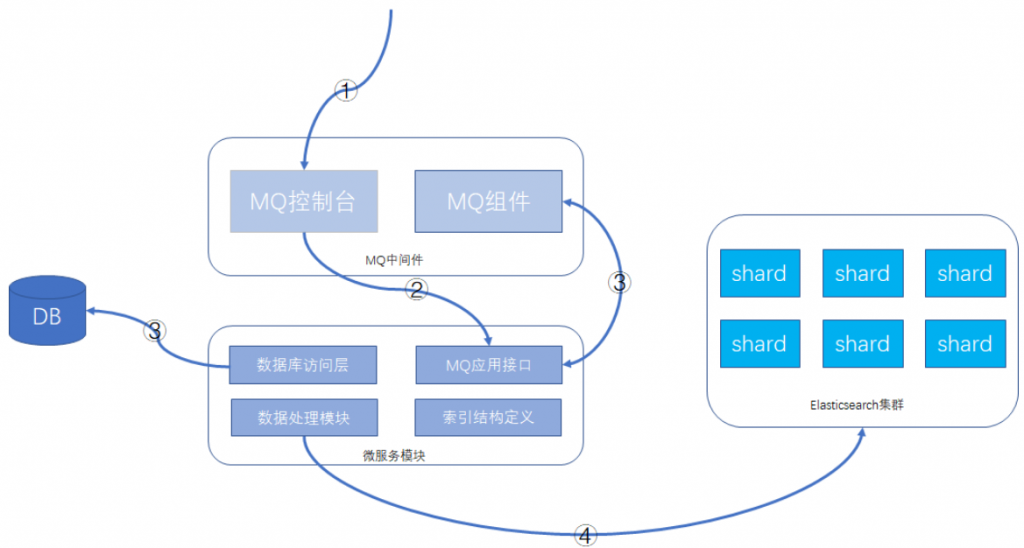
执行步骤
建议的功能方案:数据库 + MQ + 应用模块 + Elasticsearch,可以在MQ控制台发送MQ消息来触发重导数据,按批次对数据进行导入,整个过程异步化处理,请求操作示意如下所示:
详细操作步骤
- 通过MQ的web控制台或cli命令行,发送指定的MQ消息
- MQ消息被微服务模块的消费者消费,触发ES数据重新导入功能
- 微服务模块从数据库里查询数据的总数及批次信息,并将每个数据批次的分页信息重新发送给MQ消息,分页信息包含查询条件和偏移量,此MQ消息还是会被微服务的MQ消息者接收处理
- 微服务根据接收的查询条件和分页信息,从数据库获取到数据后,根据索引结构的定义,将数据组装成ES支持的JSON格式,并执行
bulk命令,将数据发送给Elasticsearch集群
这样就可以完成索引的重建工作。
方案特点
MQ中间件的选型不做具体要求,常见的RabitMQ、ActiveMQ、RocketMQ等均可。
在微服务模块方面,提供MQ消息处理接口、数据处理模块需要事先开发的,一般是创建新的索引时,配套把重建的功能也一起做好。整体功能共用一个Topic,针对每个索引,有单独的结构定义和MQ消息处理tag,代码尽可能复用。处理的批次大小需要根据实际的情况设置。
微服务模块实例会部署多个,数据是分批处理的,批次信息会一次性全部先发送给MQ,各个实例处理的数据相互不重叠,利用MQ消息的异步处理机制,可以充分利用并发的优势,加快数据重建的速度。
方案缺点
- 对数据库造成读取压力,短时间内大量的读操作,会占用数据库的硬件资源,严重时可能引起数据库性能下降
- 网络带宽占用多,数据毕竟是从一个库传到另一个库,虽说是内网,但大量的数据传输带宽占用也需要注意
- 数据重建时间稍长,跟迁移的数据量大小有关
方案二 基于scroll+bulk+索引别名方案
整体介绍
利用Elasticsearch自带的一些工具完成索引的重建工作,当然在方案实际落地时,可能也会依赖客户端的一些功能,比如用Java客户端持续的做scroll查询、bulk命令的封装等。数据完全自给自足,不依赖其他数据源。
执行步骤
假设原索引名称是book,新的索引名称为book_new,Java客户端使用别名book_alias连接Elasticsearch,该别名指向原索引book。
- 若Java客户端没有使用别名,需要给客户端分配一个:
PUT /book/_alias/book_alias - 新建索引book_new,将mapping信息,settings信息等按新的要求全部定义好
- 使用
scrollapi将数据批量查询出来
为了使用scroll,初始搜索请求应该在查询中指定scroll参数,这可以告诉Elasticsearch需要保持搜索的上下文环境多久,1m就是一分钟。
GET /book/_search?scroll=1m
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"sort": [
"_doc"
],
"size": 2
}- 采用
bulkapi将scoll查出来的一批数据,批量写入新索引
POST /_bulk
{ "index": { "_index": "book_new", "_id": "对应的id值" }}
{ 查询出来的数据值 }- 反复执行修改后的步骤3和步骤4,查询一批导入一批,以后可以借助Java Client或其他语言的API支持
注意做3时需要指定上一次查询的scroll_id:
GET /_search/scroll
{
"scroll": "1m",
"scroll_id": "步骤三中查询出来的值"
}- 切换别名book_alias到新的索引book_new上面,此时Java客户端仍然使用别名访问,也不需要修改任何代码,不需要停机
POST /_aliases
{
"actions": [
{
"remove": {
"index": "book",
"alias": "book_alias"
}
},
{
"add": {
"index": "book_new",
"alias": "book_alias"
}
}
]
}- 验证别名查询的是否为新索引的数据
方案特点
在数据传输上基本自给自足,不依赖于其他数据源,Java客户端不需要停机等待数据迁移,网络传输占用带宽较小。只是scroll查询和bulk提交这部分,数据量大时需要依赖一些客户端工具。
补充一点
在Java客户端或其他客户端访问Elasticsearch集群时,使用别名是一个好习惯。
方案三 Reindex API方案
Elasticsearch v6.3.1已经支持Reindex API,它对scroll、bulk做了一层封装,能够对文档重建索引而不需要任何插件或外部工具。
最基础的命令
POST _reindex
{
"source": {
"index": "book"
},
"dest": {
"index": "book_new"
}
}响应结果:
{
"took" : 275,
"timed_out" : false,
"total" : 4,
"updated" : 0,
"created" : 4,
"deleted" : 0,
"batches" : 1,
"version_conflicts" : 0,
"noops" : 0,
"retries" : {
"bulk" : 0,
"search" : 0
},
"throttled_millis" : 0,
"requests_per_second" : -1.0,
"throttled_until_millis" : 0,
"failures" : [ ]
}注意: 如果不手动创建新索引book_new的mapping信息,那么Elasticsearch将启动自动映射模板对数据进行类型映射,可能不是期望的类型,这点要注意一下。
version_type 属性
使用reindex api也是创建快照后再执行迁移的,这样目标索引的数据可能会与原索引有差异,version_type属性可以决定乐观锁并发处理的规则。
reindex api可以设置version_type属性,如下:
POST _reindex
{
"source": {
"index": "book"
},
"dest": {
"index": "book_new",
"version_type": "internal"
}
}version_type属性含义如下:
- internal:直接拷贝文档到目标索引,对相同的type、文档ID直接进行覆盖,默认值
- external:迁移文档到目标索引时,保留version信息,对目标索引中不存在的文档进行创建,已存在的文档按version进行更新,遵循乐观锁机制
op_type 属性和 conflicts 属性
如果op_type设置为create,那么迁移时只在目标索引中创建ID不存在的文档,已存在的文档,会提示错误,如下请求:
POST _reindex
{
"source": {
"index": "book"
},
"dest": {
"index": "book_new",
"op_type": "create"
}
}如果加上"conflicts": "proceed"配置项,那么冲突信息将不展示,只展示冲突的文档数量,请求和响应:
POST _reindex
{
"conflicts": "proceed",
"source": {
"index": "book"
},
"dest": {
"index": "book_new",
"op_type": "create"
}
}query 支持
reindex api支持数据过滤、数据排序、size设置、_source选择等,也支持脚本执行,这里提供一个简单示例:
POST _reindex
{
"size": 100,
"source": {
"index": "book",
"query": {
"term": {
"language": "english"
}
},
"sort": {
"likes": "desc"
}
},
"dest": {
"index": "book_new"
}
}小结
零停机索引重建操作的三个方案,从自研功能、scroll+bulk到reindex,我们作为Elasticsearch的使用者,三个方案的参与度是逐渐弱化的,但稳定性却是逐渐上升的,我们需要清楚地去了解各个方案的优劣,适宜的场景,然后根据实际的情况去权衡,哪个方案更适合我们的业务模型。
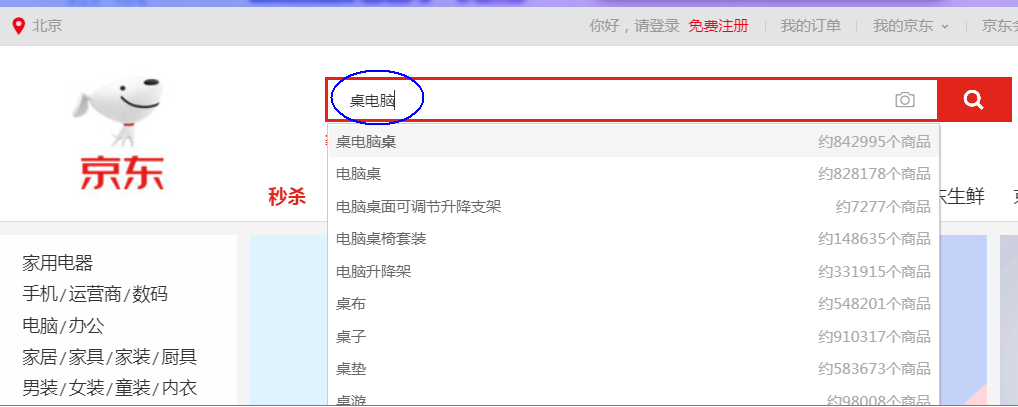
智能搜索建议
现代的搜索引擎,一般会具备"Suggest As You Type"功能,即在用户输入搜索的过程中,进行自动补全或者纠错。 通过协助用户输入更精准的关键词,提高后续全文搜索阶段文档匹配的程度。例如在京东上输入部分关键词,甚至输入拼写错误的关键词时,它依然能够提示出用户想要输入的内容:
如果自己亲手去试一下,可以看到京东在用户刚开始输入的时候是自动补全的,而当输入到一定长度,如果因为单词拼写错误无法补全,就开始尝试提示相似的词。
那么类似的功能在Elasticsearch里如何实现呢? 答案就在Suggesters API。 Suggesters基本的运作原理是将输入的文本分解为token,然后在索引的字典里查找相似的term并返回。 根据使用场景的不同,Elasticsearch里设计了4种类别的Suggester,分别是:
- Term Suggester
- Phrase Suggester
- Completion Suggester
- Context Suggester
在官方的参考文档里,对这4种Suggester API都有比较详细的介绍,下面的案例将在Elasticsearch 7.x上通过示例讲解Suggester的基础用法,希望能帮助部分国内开发者快速用于实际项目开发。
首先来看一个Term Suggester的示例:
准备一个叫做blogs的索引,配置一个text字段:
PUT /blogs
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"body": {
"type": "text"
}
}
}
}通过bulk api写入几条文档:
POST _bulk/?refresh=true
{"index":{"_index":"blogs"}}
{"body":"Lucene is cool"}
{"index":{"_index":"blogs"}}
{"body":"Elasticsearch builds on top of lucene"}
{"index":{"_index":"blogs"}}
{"body":"Elasticsearch rocks"}
{"index":{"_index":"blogs"}}
{"body":"Elastic is the company behind ELK stack"}
{"index":{"_index":"blogs"}}
{"body":"elk rocks"}
{"index":{"_index":"blogs"}}
{"body":"elasticsearch is rock solid"}此时blogs索引里已经有一些文档了,可以进行下一步的探索。为帮助理解,我们先看看哪些term会存在于词典里。
将输入的文本分析一下:
POST _analyze
{
"text": [
"Lucene is cool",
"Elasticsearch builds on top of lucene",
"Elasticsearch rocks",
"Elastic is the company behind ELK stack",
"elk rocks",
"elasticsearch is rock solid"
]
}这些分出来的token都会成为词典里一个term,注意有些token会出现多次,因此在倒排索引里记录的词频会比较高,同时记录的还有这些token在原文档里的偏移量和相对位置信息。执行一次suggester搜索看看效果:
POST /blogs/_search
{
"suggest": {
"my-suggestion": {
"text": "lucne rock",
"term": {
"suggest_mode": "missing",
"field": "body"
}
}
}
}suggest就是一种特殊类型的搜索,DSL内部的"text"指的是api调用方提供的文本,也就是通常用户界面上用户输入的内容。这里的lucne是错误的拼写,模拟用户输入错误。 "term"表示这是一个term suggester。 "field"指定suggester针对的字段,另外有一个可选的"suggest_mode"。 范例里的"missing"实际上就是缺省值,它是什么意思?有点挠头… 还是先看看返回结果吧:
{
"took" : 25,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 0,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : null,
"hits" : [ ]
},
"suggest" : {
"my-suggestion" : [
{
"text" : "lucne",
"offset" : 0,
"length" : 5,
"options" : [
{
"text" : "lucene",
"score" : 0.8,
"freq" : 2
}
]
},
{
"text" : "rock",
"offset" : 6,
"length" : 4,
"options" : [ ]
}
]
}
}在返回结果里"suggest" -> "my-suggestion"部分包含了一个数组,每个数组项对应从输入文本分解出来的token(存放在"text"这个key里)以及为该token提供的建议词项(存放在options数组里)。 示例里返回了"lucne","rock"这2个词的建议项(options),其中"rock"的options是空的,表示没有可以建议的选项,为什么? 上面提到了,我们为查询提供的suggest mode是"missing",由于"rock"在索引的词典里已经存在了,够精准,就不建议啦。 只有词典里找不到词,才会为其提供相似的选项。
如果将"suggest_mode"换成"popular"会是什么效果?
尝试一下,重新执行查询,返回结果里"rock"这个词的option不再是空的,而是建议为rocks。
{
"took" : 3,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 0,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : null,
"hits" : [ ]
},
"suggest" : {
"my-suggestion" : [
{
"text" : "lucne",
"offset" : 0,
"length" : 5,
"options" : [
{
"text" : "lucene",
"score" : 0.8,
"freq" : 2
}
]
},
{
"text" : "rock",
"offset" : 6,
"length" : 4,
"options" : [
{
"text" : "rocks",
"score" : 0.75,
"freq" : 2
}
]
}
]
}
}回想一下,rock和rocks在索引词典里都是有的。 不难看出即使用户输入的token在索引的词典里已经有了,但是因为存在一个词频更高的相似项,这个相似项可能是更合适的,就被挑选到options里了。最后还有一个"always" mode,其含义是不管token是否存在于索引词典里都要给出相似项。
有人可能会问,两个term的相似性是如何判断的? ES使用了一种叫做Levenstein edit distance的算法,其核心思想就是一个词改动多少个字符就可以和另外一个词一致。 Term suggester还有其他很多可选参数来控制这个相似性的模糊程度,这里就不一一赘述了。
Phrase suggester在Term suggester的基础上,会考量多个term之间的关系,比如是否同时出现在索引的原文里,相邻程度,以及词频等等。看个范例就比较容易明白了:
POST /blogs/_search
{
"suggest": {
"my-suggestion": {
"text": "lucne and elasticsear rock",
"phrase": {
"field": "body",
"highlight": {
"pre_tag": "<em>",
"post_tag": "</em>"
}
}
}
}
}返回结果:
{
"took" : 19,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 0,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : null,
"hits" : [ ]
},
"suggest" : {
"my-suggestion" : [
{
"text" : "lucne and elasticsear rock",
"offset" : 0,
"length" : 26,
"options" : [
{
"text" : "lucene and elasticsearch rock",
"highlighted" : "<em>lucene</em> and <em>elasticsearch</em> rock",
"score" : 0.004993905
},
{
"text" : "lucne and elasticsearch rock",
"highlighted" : "lucne and <em>elasticsearch</em> rock",
"score" : 0.0033391973
},
{
"text" : "lucene and elasticsear rock",
"highlighted" : "<em>lucene</em> and elasticsear rock",
"score" : 0.0029183894
}
]
}
]
}
}
options直接返回一个phrase列表,由于加了highlight选项,被替换的term会被高亮。因为lucene和elasticsearch曾经在同一条原文里出现过,同时替换2个term的可信度更高,所以打分较高,排在第一位返回。Phrase suggester有相当多的参数用于控制匹配的模糊程度,需要根据实际应用情况去挑选和调试。
下面来谈一下Completion Suggester,它主要针对的应用场景就是"Auto Completion"。 此场景下用户每输入一个字符的时候,就需要即时发送一次查询请求到后端查找匹配项,在用户输入速度较高的情况下对后端响应速度要求比较苛刻。因此实现上它和前面两个Suggester采用了不同的数据结构,索引并非通过倒排来完成,而是将analyze过的数据编码成FST和索引一起存放。对于一个open状态的索引,FST会被ES整个装载到内存里的,进行前缀查找速度极快。但是FST只能用于前缀查找,这也是Completion Suggester的局限所在。
为了使用Completion Suggester,字段的类型需要专门定义如下:
PUT /blogs_completion/
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"body": {
"type": "completion"
}
}
}
}用bulk API索引点数据:
POST _bulk/?refresh=true
{"index":{"_index":"blogs_completion"}}
{"body":"Lucene is cool"}
{"index":{"_index":"blogs_completion"}}
{"body":"Elasticsearch builds on top of lucene"}
{"index":{"_index":"blogs_completion"}}
{"body":"Elasticsearch rocks"}
{"index":{"_index":"blogs_completion"}}
{"body":"Elastic is the company behind ELK stack"}
{"index":{"_index":"blogs_completion"}}
{"body":"the elk stack rocks"}
{"index":{"_index":"blogs_completion"}}
{"body":"elasticsearch is rock solid"}查找:
POST /blogs_completion/_search?pretty
{
"size": 0,
"suggest": {
"blog-suggest": {
"prefix": "elastic i",
"completion": {
"field": "body"
}
}
}
}结果:
{
"took" : 14,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 0,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : null,
"hits" : [ ]
},
"suggest" : {
"blog-suggest" : [
{
"text" : "elastic i",
"offset" : 0,
"length" : 9,
"options" : [
{
"text" : "Elastic is the company behind ELK stack",
"_index" : "blogs_completion",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "lNbSf30B1ct5FZWHFp4M",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"body" : "Elastic is the company behind ELK stack"
}
}
]
}
]
}
}值得注意的一点是Completion Suggester在索引原始数据的时候也要经过analyze阶段,取决于选用的analyzer不同,某些词可能会被转换,某些词可能被去除,这些会影响FST编码结果,也会影响查找匹配的效果。
比如我们删除上面的索引,重新设置索引的mapping,将analyzer更改为"english":
DELETE /blogs_completion
PUT /blogs_completion
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"body": {
"type": "completion",
"analyzer": "english"
}
}
}
}
POST _bulk/?refresh=true
{"index":{"_index":"blogs_completion"}}
{"body":"Lucene is cool"}
{"index":{"_index":"blogs_completion"}}
{"body":"Elasticsearch builds on top of lucene"}
{"index":{"_index":"blogs_completion"}}
{"body":"Elasticsearch rocks"}
{"index":{"_index":"blogs_completion"}}
{"body":"Elastic is the company behind ELK stack"}
{"index":{"_index":"blogs_completion"}}
{"body":"the elk stack rocks"}
{"index":{"_index":"blogs_completion"}}
{"body":"elasticsearch is rock solid"}bulk api索引同样的数据后,执行下面的查询:
POST /blogs_completion/_search?pretty
{
"size": 0,
"suggest": {
"blog-suggest": {
"prefix": "elastic i",
"completion": {
"field": "body"
}
}
}
}居然没有匹配结果了,多么费解! 原来我们用的english analyzer会剥离掉stop word,而is就是其中一个,被剥离掉了!
用analyze api测试一下:
POST _analyze
{
"text": "elasticsearch is rock solid",
"analyzer": "english"
}
# 会发现只有3个token:
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "elasticsearch",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 13,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "rock",
"start_offset" : 17,
"end_offset" : 21,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 2
},
{
"token" : "solid",
"start_offset" : 22,
"end_offset" : 27,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 3
}
]
}FST(Finite StateTransducers)只编码了这3个token,并且默认的还会记录他们在文档中的位置和分隔符。 用户输入"elastic i"进行查找的时候,输入被分解成"elastic"和"i",FST没有编码这个“i” , 匹配失败。
好吧,如果你现在还足够清醒的话,试一下搜索"elastic is",会发现又有结果,why? 因为这次输入的text经过english analyzer的时候is也被剥离了,只需在FST里查询"elastic"这个前缀,自然就可以匹配到了。
其他能影响completion suggester结果的,还有如"preserve_separators","preserve_position_increments"等等mapping参数来控制匹配的模糊程度。以及搜索时可以选用Fuzzy Queries,使得上面例子里的"elastic i"在使用english analyzer的情况下依然可以匹配到结果。
"preserve_separators": false, 这个设置为false,将忽略空格之类的分隔符
"preserve_position_increments": true,如果建议词第一个词是停用词,并且我们使用了过滤停用
词的分析器,需要将此设置为false因此用好Completion Sugester并不是一件容易的事,实际应用开发过程中,需要根据数据特性和业务需要,灵活搭配analyzer和mapping参数,反复调试才可能获得理想的补全效果。
回到篇首京东或者百度搜索框的补全/纠错功能,如果用ES怎么实现呢?我能想到的一个的实现方式:在用户刚开始输入的过程中,使用Completion Suggester进行关键词前缀匹配,刚开始匹配项会比较多,随着用户输入字符增多,匹配项越来越少。如果用户输入比较精准,可能Completion Suggester的结果已经够好,用户已经可以看到理想的备选项了。
如果Completion Suggester已经到了零匹配,那么可以猜测是否用户有输入错误,这时候可以尝试一下Phrase Suggester。如果Phrase Suggester没有找到任何option,开始尝试term Suggester。
精准程度上(Precision)看: Completion > Phrase > term, 而召回率上(Recall)则反之。从性能上看,Completion Suggester是最快的,如果能满足业务需求,只用Completion Suggester做前缀匹配是最理想的。 Phrase和Term由于是做倒排索引的搜索,相比较而言性能应该要低不少,应尽量控制suggester用到的索引的数据量,最理想的状况是经过一定时间预热后,索引可以全量map到内存。
召回率(Recall) = 系统检索到的相关文件 / 系统所有相关的文件总数
准确率(Precision) = 系统检索到的相关文件 / 系统所有检索到的文件总数
从一个大规模数据集合中检索文档时,可把文档分成四组:
- 系统检索到的相关文档(A)
- 系统检索到的不相关文档(B)
- 相关但是系统没有检索到的文档(C)
- 不相关且没有被系统检索到的文档(D)
则:
- 召回率R:用实际检索到相关文档数作为分子,所有相关文档总数作为分母,即R = A / ( A + C )
- 精度P:用实际检索到相关文档数作为分子,所有检索到的文档总数作为分母,即P = A / ( A + B )
举例:一个数据库有 1000 个文档,其中有 50 个文档符合相关定义的问题,系统检索到 75 个文档,但
其中只有 45 个文档被检索出
精度:P=45/75=60%
召回率:R=45/50=90%Context Suggester
- Completion Suggester的扩展
- 可以在搜索中加入更多的上下文信息,然后根据不同的上下文信息,对相同的输入,比如"star",提供不同的建议值,比如:咖啡相关:starbucks;电影相关:star wars
Elasticsearch Java Client
说明
ES提供多种不同的客户端:
TransportClient:ES提供的传统客户端,官方计划8.0版本删除此客户端RestClient RestClient:官方推荐使用,它包括两种:Java Low Level REST Client和 Java High Level REST Client。 ES在6.0之后提供 Java High Level REST Client, 两种客户端官方更推荐使用 Java High Level REST Client, 使用时加入对应版本的依赖即可
SpringBoot 中使用 RestClient
创建SpringBoot项目,添加ES客户端依赖:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<artifactId>search-engine-spring-boot</artifactId>
<groupId>com.rubin</groupId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>es-spring-boot</artifactId>
<properties>
<elasticsearch.version>7.6.0</elasticsearch.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client</artifactId>
<version>${elasticsearch.version}</version>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch</artifactId>
<version>${elasticsearch.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project><?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<modules>
<module>es-spring-boot</module>
</modules>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.1.9.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.rubin</groupId>
<artifactId>search-engine-spring-boot</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>pom</packaging>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<excludes>
<exclude>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</exclude>
</excludes>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>启动类:
package com.rubin.es.springboot;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class EsSpringBootApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(EsSpringBootApplication.class, args);
}
}
配置文件:
#多个结点中间用逗号分隔
es.hosts: es-host:9200配置类:
package com.rubin.es.springboot.config;
import org.apache.http.HttpHost;
import org.apache.http.auth.AuthScope;
import org.apache.http.auth.Credentials;
import org.apache.http.auth.UsernamePasswordCredentials;
import org.apache.http.client.CredentialsProvider;
import org.apache.http.client.config.RequestConfig;
import org.apache.http.impl.client.BasicCredentialsProvider;
import org.apache.http.impl.nio.client.HttpAsyncClientBuilder;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestClient;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestClientBuilder;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestHighLevelClient;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringBootConfiguration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
@SpringBootConfiguration
public class EsConfig {
@Value("${es.hosts}")
private String hostlist;
@Bean
public RestHighLevelClient restHighLevelClient() {
// 解析hostlist配置信息
String[] split = hostlist.split(",");
// 创建HttpHost数组,其中存放es主机和端口的配置信息
HttpHost[] httpHostArray = new HttpHost[split.length];
for (int i = 0; i < split.length; i++) {
String item = split[i];
httpHostArray[i] = new HttpHost(item.split(":")[0],
Integer.parseInt(item.split(":")[1]), "http");
}
final RestClientBuilder builder = RestClient.builder(httpHostArray);
final CredentialsProvider credentialsProvider = new BasicCredentialsProvider();
credentialsProvider.setCredentials(AuthScope.ANY, new UsernamePasswordCredentials("elastic", "RubinChu@940220"));
builder.setRequestConfigCallback(builder1 -> {
builder1.setConnectTimeout(-1);
builder1.setSocketTimeout(-1);
builder1.setConnectionRequestTimeout(-1);
return builder1;
}).setHttpClientConfigCallback(httpAsyncClientBuilder -> {
httpAsyncClientBuilder.disableAuthCaching();
return httpAsyncClientBuilder.setDefaultCredentialsProvider(credentialsProvider);
});
// 创建RestHighLevelClient客户端
return new RestHighLevelClient(builder);
}
}
测试类:
package com.rubin.es.sprngboot;
import com.rubin.es.springboot.EsSpringBootApplication;
import org.apache.lucene.search.TotalHits;
import org.elasticsearch.action.DocWriteResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.action.admin.indices.create.CreateIndexRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.admin.indices.create.CreateIndexResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.action.admin.indices.delete.DeleteIndexRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.get.GetRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.get.GetResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.action.index.IndexRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.index.IndexResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.action.search.SearchRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.search.SearchResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.action.search.SearchScrollRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.search.SearchType;
import org.elasticsearch.action.support.master.AcknowledgedResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.client.IndicesClient;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RequestOptions;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestHighLevelClient;
import org.elasticsearch.common.unit.TimeValue;
import org.elasticsearch.common.xcontent.XContentType;
import org.elasticsearch.index.query.QueryBuilders;
import org.elasticsearch.search.Scroll;
import org.elasticsearch.search.SearchHit;
import org.elasticsearch.search.SearchHits;
import org.elasticsearch.search.builder.SearchSourceBuilder;
import org.elasticsearch.search.sort.SortOrder;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
@SpringBootTest(classes = EsSpringBootApplication.class)
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
public class EsTest {
@Autowired
private RestHighLevelClient restHighLevelClient;
/**
* 创建索引库
*
* @throws IOException
*/
@Test
public void testCreateIndex() throws IOException {
// 创建一个索引创建请求对象
CreateIndexRequest createIndexRequest = new CreateIndexRequest("elasticsearch_test");
//设置映射
// XContentBuilder builder = XContentFactory.jsonBuilder()
// .startObject()
// .field("properties")
// .startObject()
// .field("description").startObject().field("type", "text").field("analyzer", "ik_max_word").endObject()
// .field("name").startObject().field("type", "keyword").endObject()
// .field("pic").startObject().field("type", "text").field("index", "false").endObject()
// .field("studymodel").startObject().field("type", "keyword").endObject()
// .endObject()
// .endObject();
// createIndexRequest.mapping("doc", builder);
createIndexRequest.mapping("_doc", "{\n" +
" \"properties\": {\n" +
" \"description\": {\n" +
" \"type\": \"text\",\n" +
" \"analyzer\": \"ik_max_word\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"name\": {\n" +
" \"type\": \"keyword\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"pic\": {\n" +
" \"type\": \"text\",\n" +
" \"index\": false\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"studymodel\": {\n" +
" \"type\": \"keyword\"\n" +
" }\n" +
" }\n" +
" }", XContentType.JSON);
// 操作索引的客户端
IndicesClient indicesClient = restHighLevelClient.indices();
CreateIndexResponse createIndexResponse = indicesClient.create(createIndexRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
// 得到响应
boolean acknowledged = createIndexResponse.isAcknowledged();
System.out.println(acknowledged);
}
/**
* 删除索引库
*
* @throws IOException
*/
@Test
public void testDeleteIndex() throws IOException {
// 构建 删除索引库的请求对象
DeleteIndexRequest deleteIndexRequest = new DeleteIndexRequest("elasticsearch_test");
IndicesClient indicesClient = restHighLevelClient.indices();
AcknowledgedResponse deleteResponse = indicesClient.delete(deleteIndexRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
// 得到响应
boolean acknowledge = deleteResponse.isAcknowledged();
System.out.println(acknowledge);
}
/**
* 添加文档
*
* @throws IOException
*/
@Test
public void testAddDoc() throws IOException {
// 准备索取请求对象
//IndexRequest indexRequest = new IndexRequest("elasticsearch_test","doc");
IndexRequest indexRequest = new IndexRequest("elasticsearch_test");
//indexRequest.id("2");
// 文档内容 准备json数据
Map<String, Object> jsonMap = new HashMap<>();
jsonMap.put("name", "spring cloud实战3");
jsonMap.put("description", "本课程主要从四个章节进行讲解3: 1.微服务架构入门 2.spring cloud 基础入门 3.实战Spring Boot 4.注册中心eureka。");
jsonMap.put("studymodel", "3101001");
jsonMap.put("timestamp", "2020-07-22 20:09:18");
jsonMap.put("price", 35.6);
indexRequest.source(jsonMap);
// 执行请求
IndexResponse indexResponse = restHighLevelClient.index(indexRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
DocWriteResponse.Result result = indexResponse.getResult();
System.out.println(result);
}
/**
* 查询文档
*
* @throws IOException
*/
@Test
public void testGetDoc() throws IOException {
// 查询请求对象
GetRequest getRequest = new GetRequest("elasticsearch_test", "ndbFiH0B1ct5FZWH2p7M");
GetResponse getResponse = restHighLevelClient.get(getRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
// 得到文档内容
Map<String, Object> sourceMap = getResponse.getSourceAsMap();
System.out.println(sourceMap);
}
/**
* 搜索全部记录
*
* @throws IOException
*/
@Test
public void testSearchAll() throws IOException {
// 搜索请求对象
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest("elasticsearch_test");
searchRequest.searchType(SearchType.QUERY_THEN_FETCH);
// 搜索源构建对象
SearchSourceBuilder searchSourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
// 设置搜索方法
searchSourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery());
searchSourceBuilder.fetchSource(new String[]{"name", "price", "timestamp", "description"}, new String[]{});
// 请求对象设置 搜索源对象
searchRequest.source(searchSourceBuilder);
// 使用client 执行搜索
SearchResponse searchResponse = restHighLevelClient.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
// 搜索结果
SearchHits hits = searchResponse.getHits();
// 匹配到的总记录数
TotalHits totalHits = hits.getTotalHits();
System.out.println("查询到的总记录数:" + totalHits.value);
// 得到的匹配度高的文档
SearchHit[] searchHits = hits.getHits();
for (SearchHit hit : searchHits) {
String id = hit.getId();
System.out.println(id);
// 源文档的内容
Map<String, Object> sourceMap = hit.getSourceAsMap();
String name = (String) sourceMap.get("name");
String timestamp = (String) sourceMap.get("timestamp");
String description = (String) sourceMap.get("description");
Double price = (Double) sourceMap.get("price");
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(timestamp);
System.out.println(description);
System.out.println(price);
}
}
/**
* 词条搜索
*
* @throws IOException
*/
@Test
public void testTermQuery() throws IOException {
// 搜索请求对象
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest("elasticsearch_test");
// 搜索源构建对象
SearchSourceBuilder searchSourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
// 设置搜索方法
//searchSourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.termQuery("name","spring cloud实战"));
searchSourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.termQuery("description", "spring"));
searchSourceBuilder.fetchSource(new String[]{"name", "price", "timestamp"}, new String[]{});
// 请求对象设置 搜索源对象
searchRequest.source(searchSourceBuilder);
// 使用client 执行搜索
SearchResponse searchResponse = restHighLevelClient.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
// 搜索结果
SearchHits hits = searchResponse.getHits();
// 匹配到的总记录数
TotalHits totalHits = hits.getTotalHits();
System.out.println("查询到的总记录数:" + totalHits.value);
// 得到的匹配度高的文档
SearchHit[] searchHits = hits.getHits();
for (SearchHit hit : searchHits) {
String id = hit.getId();
// 源文档的内容
Map<String, Object> sourceMap = hit.getSourceAsMap();
String name = (String) sourceMap.get("name");
String timestamp = (String) sourceMap.get("timestamp");
String description = (String) sourceMap.get("description");
Double price = (Double) sourceMap.get("price");
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(timestamp);
System.out.println(description);
System.out.println(price);
}
}
/**
* 分页搜索所有
*
* @throws IOException
*/
@Test
public void testSearchAllPage() throws IOException {
// 搜索请求对象
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest("elasticsearch_test");
// 搜索源构建对象
SearchSourceBuilder searchSourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
// 设置搜索方法
searchSourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery());
searchSourceBuilder.fetchSource(new String[]{"name", "price", "timestamp"}, new String[]{});
// 设置分页参数
int page = 2;
int size = 2;
// 计算出 from
int form = (page - 1) * size;
searchSourceBuilder.from(form);
searchSourceBuilder.size(size);
// 设置price 降序
searchSourceBuilder.sort("price", SortOrder.DESC);
// 请求对象设置 搜索源对象
searchRequest.source(searchSourceBuilder);
// 使用client 执行搜索
SearchResponse searchResponse = restHighLevelClient.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
// 搜索结果
SearchHits hits = searchResponse.getHits();
// 匹配到的总记录数
TotalHits totalHits = hits.getTotalHits();
System.out.println("查询到的总记录数:" + totalHits.value);
// 得到的匹配度高的文档
SearchHit[] searchHits = hits.getHits();
for (SearchHit hit : searchHits) {
String id = hit.getId();
System.out.println(id);
// 源文档的内容
Map<String, Object> sourceMap = hit.getSourceAsMap();
String name = (String) sourceMap.get("name");
String timestamp = (String) sourceMap.get("timestamp");
String description = (String) sourceMap.get("description");
Double price = (Double) sourceMap.get("price");
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(timestamp);
System.out.println(description);
System.out.println(price);
}
}
/**
* 分页词条查询
*
* @throws IOException
*/
@Test
public void testTermQueryPage() throws IOException {
// 搜索请求对象
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest("elasticsearch_test");
// 搜索源构建对象
SearchSourceBuilder searchSourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
// 设置搜索方法
searchSourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.termQuery("name", "spring cloud实战"));
searchSourceBuilder.fetchSource(new String[]{"name", "price", "timestamp"}, new String[]{});
// 设置分页参数
int page = 1;
int size = 2;
// 计算出 from
int form = (page - 1) * size;
searchSourceBuilder.from(form);
searchSourceBuilder.size(size);
// 设置price 降序
searchSourceBuilder.sort("price", SortOrder.DESC);
// 请求对象设置 搜索源对象
searchRequest.source(searchSourceBuilder);
// 使用client 执行搜索
SearchResponse searchResponse = restHighLevelClient.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
// 搜索结果
SearchHits hits = searchResponse.getHits();
// 匹配到的总记录数
TotalHits totalHits = hits.getTotalHits();
System.out.println("查询到的总记录数:" + totalHits.value);
// 得到的匹配度高的文档
SearchHit[] searchHits = hits.getHits();
for (SearchHit hit : searchHits) {
String id = hit.getId();
// 源文档的内容
Map<String, Object> sourceMap = hit.getSourceAsMap();
String name = (String) sourceMap.get("name");
String timestamp = (String) sourceMap.get("timestamp");
String description = (String) sourceMap.get("description");
Double price = (Double) sourceMap.get("price");
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(timestamp);
System.out.println(description);
System.out.println(price);
}
}
/**
* 滚动搜索示例
*
* @param scrollId
* @return
*/
public List<Map<String, Object>> searchQuestionBO(String scrollId) {
// 搜索请求对象
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest("elasticsearch_test");
// 搜索源构建对象
SearchSourceBuilder searchSourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
// 设置搜索方法
searchSourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.termQuery("name", "spring cloud实战"));
searchSourceBuilder.fetchSource(new String[]{"name", "price", "timestamp"}, new String[]{});
// 设置price 降序
searchSourceBuilder.sort("price", SortOrder.DESC);
// 请求对象设置 搜索源对象
searchRequest.source(searchSourceBuilder);
List<Map<String, Object>> questionBOList = new ArrayList<>();
SearchResponse searchResponse = null;
boolean deepSearch = false;
try {
deepSearch = true;
searchRequest.source().size(2);
final Scroll scroll = new Scroll(TimeValue.timeValueMinutes(30L));
searchRequest.scroll(scroll);
searchResponse = restHighLevelClient.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
SearchScrollRequest scrollRequest = new SearchScrollRequest(scrollId);
scrollRequest.scroll(scroll);
searchResponse = restHighLevelClient.scroll(scrollRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
SearchHits searchHits = searchResponse.getHits();
SearchHit[] searchHit = searchHits.getHits();
long total = searchHits.getTotalHits().value;
for (int i = 0; i < searchHit.length; i++) {
SearchHit item = searchHit[i];
questionBOList.add(item.getSourceAsMap());
}
return questionBOList;
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return questionBOList;
}
}
以上就是本文的全部内容。欢迎小伙伴们积极留言交流~~~
文章评论